Volume 11, Number 12—December 2005
Letter
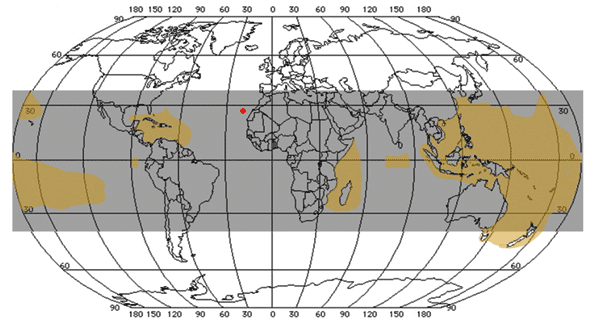
Ciguatera Fish Poisoning, Canary Islands
Figure
References
- Ting JY, Brown AF. Ciguatera poisoning: a global issue with common management problems. Eur J Emerg Med. 2001;8:295–300. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pearn J. Neurology of ciguatera. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001;70:4–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Juranovic LR, Park DL. Foodborne toxins of marine origin: ciguatera. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 1991;117:51–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Puente S, Lago M, Subirats M, González Lahoz JM. Ciguatera: un caso importado. Med Clin (Barc). 1995;104:357.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Glaziou P, Legrand AM. The epidemiology of ciguatera fish poisoning. Toxicon. 1994;32:863–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dickey R, Jester E, Granade R, Mowdy D, Moncreiff C, Rebarchik D, Monitoring brevetoxins during a Gymnodinium breve red tide: comparison of sodium channel specific cytotoxicity assay and mouse bioassay for determination of neurotoxic shellfish toxins in shellfish extracts. Nat Toxins. 1999;7:157–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pottier I, Hamilton B, Jones A, Lewis RJ, Vernoux JP. Identification of slow and fast-acting toxins in a highly ciguatoxic barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) by HPLC/MS and radiolabelled ligand binding. Toxicon. 2003;42:663–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pérez CM, Vásquez PA, Perret CF. Treatment of ciguatera poisoning with gabapentin. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:692–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: February 02, 2012
Page updated: February 02, 2012
Page reviewed: February 02, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.