Volume 11, Number 3—March 2005
Dispatch
Concomitant Tickborne Encephalitis and Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis
Figure
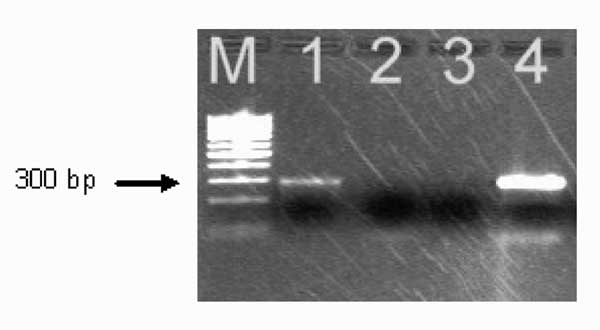
Figure. . Polymerase chain reaction amplification of Anaplasma phagocytophilum DNA from the patient's acute-phase blood sample. Amplified DNA was separated by electrophoresis through the 2% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide. Lane 1, patient sample (note the presence of the band at ≈293 bp); lane 2, negative sample; lane 3, negative control (no-DNA template control); lane 4 positive control (DNA extracted from the cultured isolate of A. phagocytophilum). Lane M represents a 100-bp DNA ladder for estimation of molecular sizes.
Page created: April 25, 2012
Page updated: April 25, 2012
Page reviewed: April 25, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.