Volume 12, Number 10—October 2006
Dispatch
Fourth Human Parechovirus Serotype
Figure 1
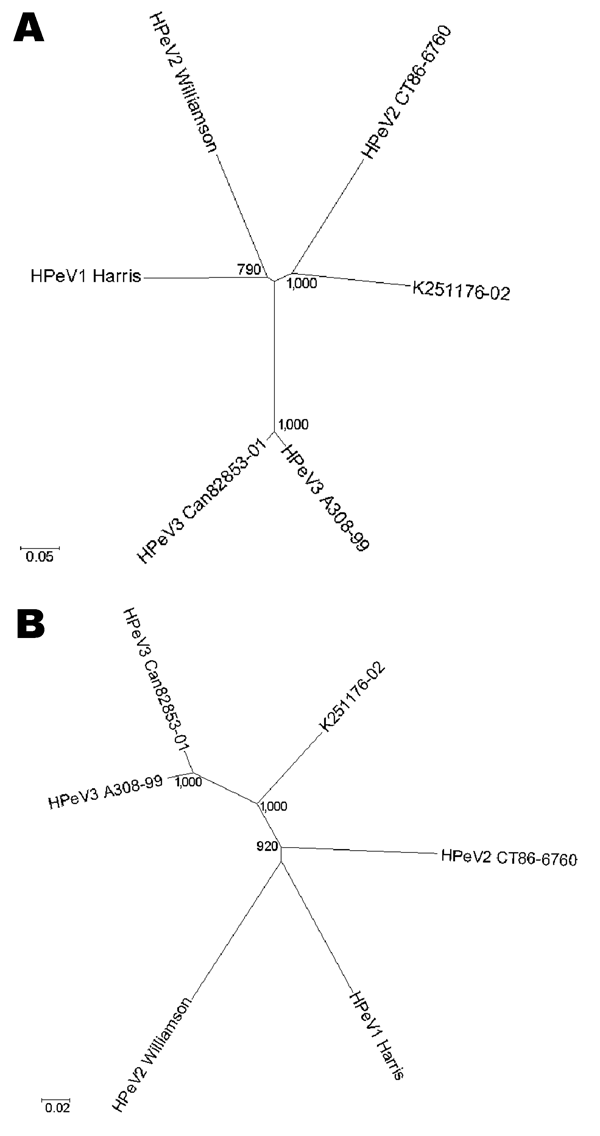
Figure 1. Unrooted phylogenetic trees showing the relationship between K251176-02 (DQ315670) and the prototype strains human parechovirus serotype 1 (HPeV1) Harris (S45208), HPeV2 Williamson (AJ005695), HPeV2 CT86-6760 (AF055846), HPeV3 A308-99 (AB084913), and Can82853-01 (AJ889918) based on nucleotide Jukes and Cantor substitution model for the capsid region (A) and the nonstructural region (B). The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method as implemented in MEGA version 3.1. Gaps introduced for optimal alignment were not considered informative and were excluded from the analyses by complete deletion. Numbers represent the frequency of occurrence of nodes in 1,000 bootstrap replicas. The use of other evolution models did not influence the tree topology.