Volume 12, Number 11—November 2006
Dispatch
Food Markets with Live Birds as Source of Avian Influenza
Figure 2
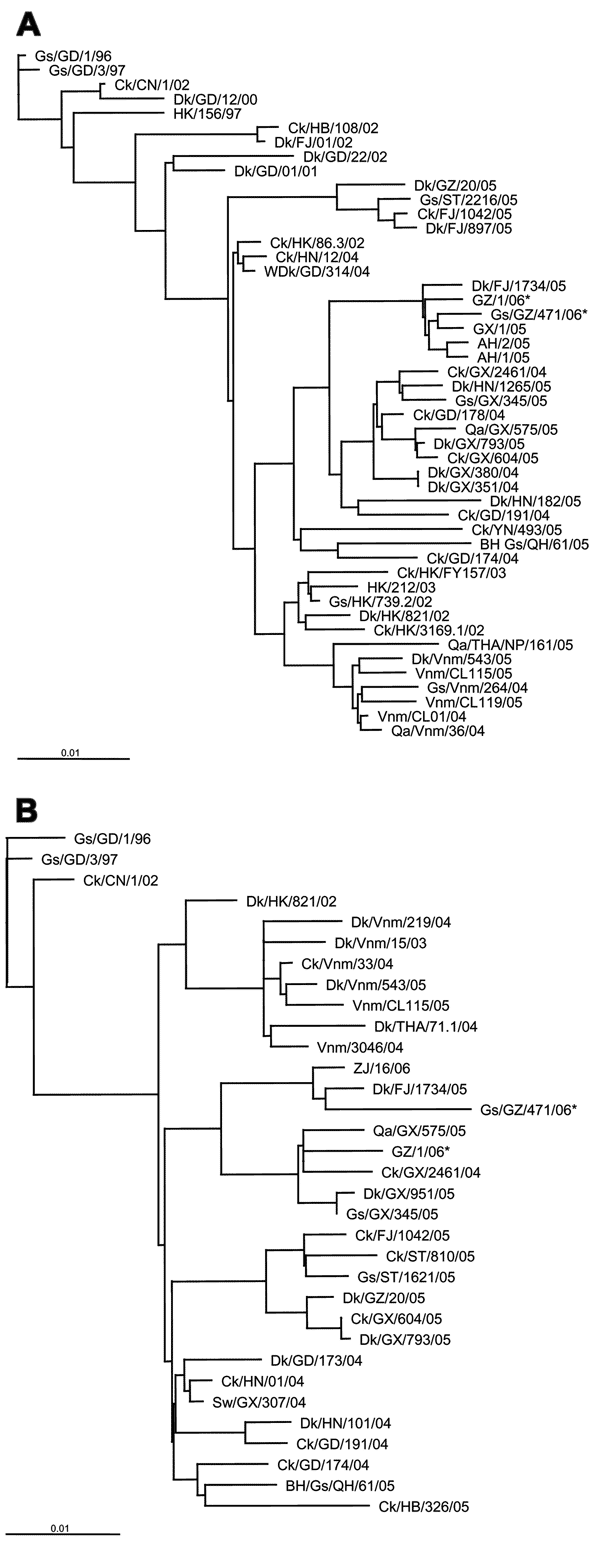
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships of representative H5N1 influenza virus strains and patient and animal cage isolates (indicated by asterisks) used in this study. A) Hemagglutinin gene (nt positions 29–1650). B) Neuramidase gene (nt positions 28–1323). Gs, goose; GD, Guangdong; Ck, chicken; CN, People's Republic of China; Dk, duck; HK, Hong Kong; HB, Hebei; FJ, Fujian; GZ, Guangzhou; ST, Shantou; HN, Hunan; WDK, wild duck; GX, Guangxi; AH, Anhui; Qa, quail; YN, Yunnan; BH Gs, brown-headed goose; QH, Qinghai; THA, Thailand, NP, Nakhon Pathom; Vnm, Vietnam; ZJ, Zhejiang; Sw, swine. Scale bars show percentage relatedness.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: October 17, 2011
Page updated: October 17, 2011
Page reviewed: October 17, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.