Volume 12, Number 12—December 2006
Dispatch
West Nile Virus in Horses, sub-Saharan Africa
Figure 2
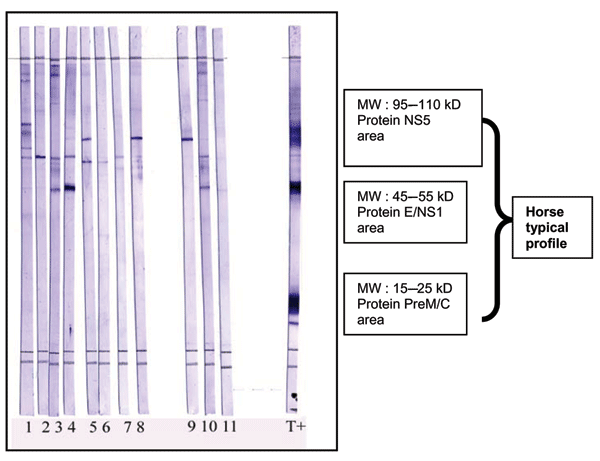
Figure 2. West Nile virus (WNV) Western blot as a validation of ELISA-positive results. Proteins from WNV-infected cells lysates were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on 13% acrylamide gels and transferred on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Strips were cut and blocked with nonfat milk (5%). Serum samples diluted (1:200) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), 5% nonfat milk, and 0.1% Tween 20 were loaded on strips and incubated for 1 h with slow shaking. Strips were washed 4 times in PBS, 0.5% Tween, and incubated for 1 h in anti-horse immunoglobulin G (IgG) peroxidase (1:8,000). After 4 washes, Western blots were incubated for 5 min with trimethylbenzidine substrate (with specific enhancer). Strips were washed once with water to stop the staining. Results were obtained within 24 h. MW, molecular weight; T+, horse from Chad with positive Western blot results; serum samples 1–11, horse from southeast France, IgG positive by ELISA but negative by neutralization; NS5, nonstructural protein 5; E, envelope; PreM, premembrane; C, capsid.