Volume 12, Number 2—February 2006
Perspective
HIV Drug-resistant Strains as Epidemiologic Sentinels
Figure 1
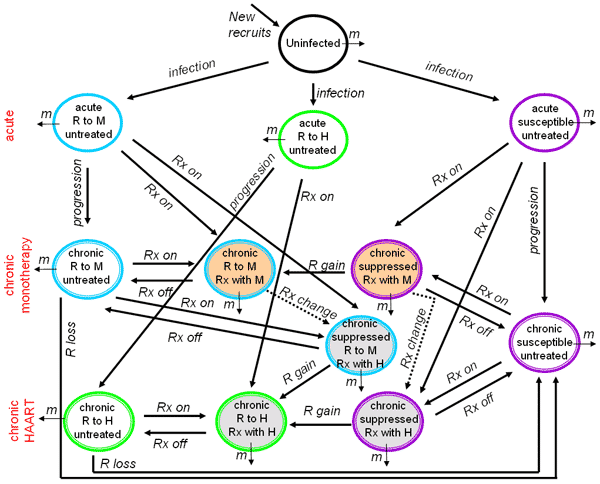
Figure 1. Flow chart of the different categories and flows considered in our model system. For simplicity, we considered 1 type of treatment when analyzing the effects of an increase in high-risk behavior and treatment delay. When considering the effects of overall change in treatment strategy, all categories and flows were included in the analysis. Abbreviations: m, mortality (composed of background deaths for all categories, and for persons in the chronic phase of infection, HIV-related deaths are included); Rx, treatment; R, resistance; M, monotherapy; H, highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Color code for the categories' encircling ovals: black (uninfected); purple (wild type); blue (monotherapy resistant strain); green (HAART-resistant strain). Background code of oval categories: no fill (untreated); tan (monotherapy); gray (HAART). Code for the categories' encircling ovals: single, no staging (uninfected and acutely infected); double, staged categories (persons in the chronic phase).