Volume 12, Number 3—March 2006
Dispatch
Aquariums as Reservoirs for Multidrug-resistant Salmonella Paratyphi B
Figure 2
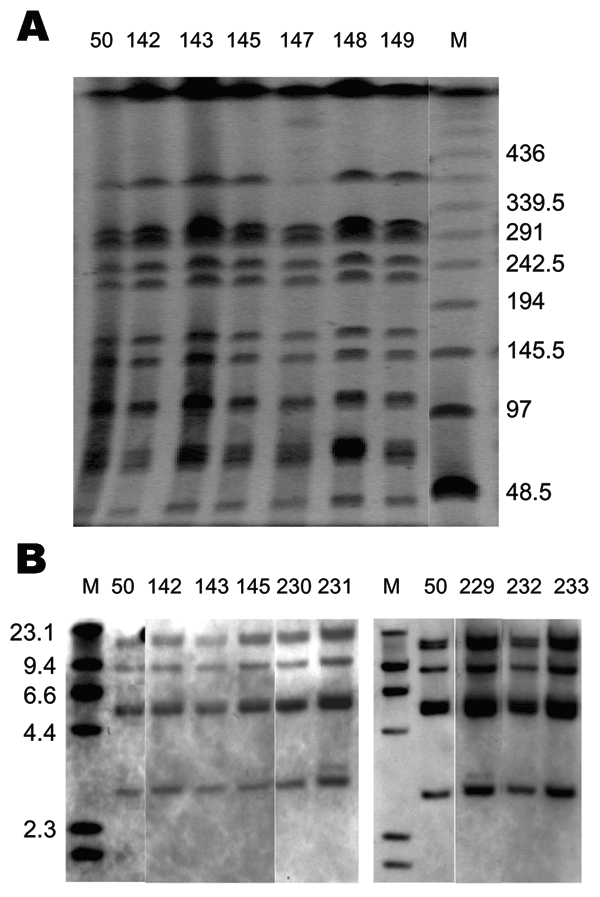
Figure 2. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and IS200 profiles of Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi B dT+ isolates positive for Salmonella genomic island 1. A) PFGE profiles. Xba I–digested whole-cell DNA was separated by PFGE as previously described (12). Molecular mass markers (lane M) are low-range PFGE markers (New England BioLabs, Beverly, MA, USA) composed of concatamers of bacteriophage lambda DNA. The band absent in lane 147 was present in other runs. B) IS200 profiles. PstI digests of whole-cell DNA were separated and hybridized with an IS200 digoxigenin (DIG)–labeled probe. Molecular mass markers (lane M) are DIG-labeled bacteriophage lambda DNA digested with HindIII (Roche Diagnostics, Castle Hill, New South Wales, Australia). Primers and polymerase chain reaction conditions used to generate the IS200 probe have been previously described (6).
References
- Chart H. The pathogenicity of strains of Salmonella Paratyphi B and Salmonella Java. J Appl Microbiol. 2003;94:340–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Van Pelt W, van der Zee H, Wannet WJ, van de Giessen AW, Mevius DJ, Bolder NM, Explosive increase of Salmonella Java in poultry in the Netherlands: consequences for public health. Euro Surveill. 2003;8:31–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miko A, Guerra B, Schroeter A, Dorn C, Helmuth R. Molecular characterization of multiresistant d-tartrate-positive Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi B isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:3184–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mulvey MR, Boyd D, Cloeckaert A, Ahmed R, Ng LK. Emergence of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Paratyphi B dT+, Canada. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:1307–10.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Threlfall J, Levent B, Hopkins KL, de Pinna E, Ward LR, Brown DJ. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella Java. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:170–1.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weill FX, Fabre L, Grandry B, Grimont PA, Casin I. Multiple-antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica serotype Paratyphi B isolates collected in France between 2000 and 2003 is due mainly to strains harboring Salmonella genomic islands 1, 1-B, and 1-C. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:2793–801. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Levings RS, Lightfoot D, Partridge SR, Hall RM, Djordjevic SP. The genomic island SGI1, containing the multiple antibiotic resistance region of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 or variants of it, is widely distributed in other S. enterica serovars. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:4401–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boyd D, Peters GA, Cloeckaert A, Boumedine KS, Chaslus-Dancla E, Imberechts H, Complete nucleotide sequence of a 43-kilobase genomic island associated with the multidrug resistance region of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 and its identification in phage type DT120 and serovar Agona. J Bacteriol. 2001;183:5725–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gaulin C, Vincent C, Alain L, Ismail J. Outbreak of Salmonella Paratyphi B linked to aquariums in the province of Quebec, 2000. Can Commun Dis Rep. 2002;28:89–93, 96.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Senanayake SN, Ferson MJ, Botham SJ, Belinfante RT. A child with Salmonella enterica serotype Paratyphi B infection acquired from a fish tank. Med J Aust. 2004;180:250.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meunier D, Boyd D, Mulvey MR, Baucheron S, Mammina C, Nastasi A, Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium DT104 antibiotic resistance genomic island I in serotype Paratyphi B. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:430–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thong KL, Ngeow YF, Altwegg M, Navaratnam P, Pang T. Molecular analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and ribotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:1070–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Goh YL, Yasin R, Puthucheary SD, Koh YT, Lim VK, Taib Z, DNA fingerprinting of human isolates of Salmonella enterica serotype Paratyphi B in Malaysia. J Appl Microbiol. 2003;95:1134–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lehane L, Rawlin GT. Topically acquired bacterial zoonoses from fish: a review. Med J Aust. 2000;173:256–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar