Volume 12, Number 5—May 2006
Letter
Postmortem Confirmation of Human Rabies Source
Figure
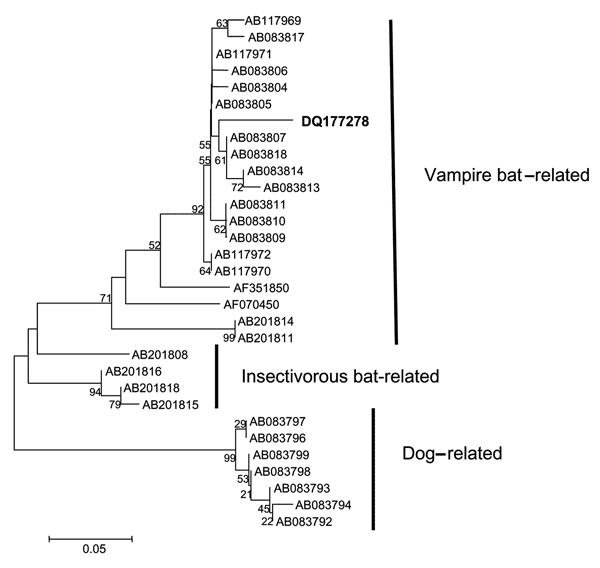
Figure. Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree to a stretch of the 3´ end of the N gene of rabies virus variants related to vampire bats, insectivorous bats, and dogs. Strain DQ177278 is shown in bold. The bar indicates the genetic distance scale. Numbers at each node indicate 1,000 replicates of bootstrap values.
Page created: January 12, 2012
Page updated: January 12, 2012
Page reviewed: January 12, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.