Volume 12, Number 6—June 2006
Research
Norwalk Virus–specific Binding to Oyster Digestive Tissues
Figure
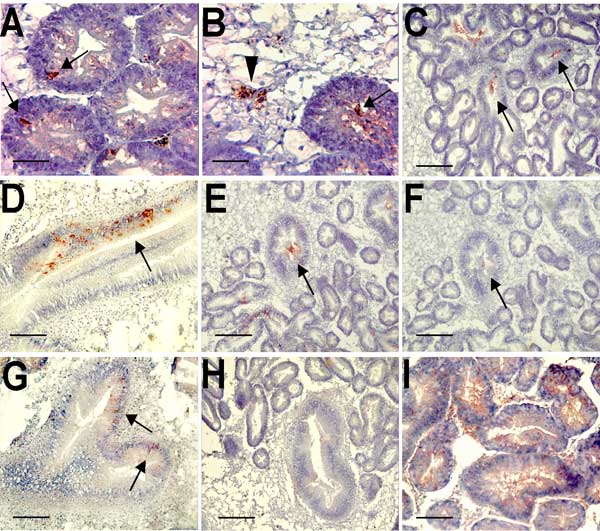
Figure. Immunohistochemical detection of Norwalk viruslike particles (VLPs) in oyster digestive tissue. A) VLPs in the digestive diverticulum 12 h after seeding sea water with 109 particles. The arrows show immunoreactivity detected in intraepithelial cells. B) VLPs in the digestive diverticulum 12 h after seeding sea water with 1012 particles. The arrowhead shows immunoreactivity in a phagocyte located in connective tissue, and the arrow shows immunoreactivity in the lumen of a digestive tubule. C) Attachment of recombinant VLPs to secondary ducts of the digestive diverticula after incubation on tissue sections. The arrows show immunoreactivity in the lumen of ducts. D) Attachment of Norwalk virus to a main digestive duct. The arrow shows immunoreactivity in epithelial duct cells. E and F) Attachment (arrows) of recombinant VLPs to digestive ducts without (E) or with (F) periodate treatment of serial tissue sections. G) Binding of VLPs (arrows) to a main digestive duct of VLPs from the H331A mutant capsid protein. H) Lack of binding of the H329A mutant. I) Binding of HPA lectin to the digestive diverticula. Scale bars: A and B, 10 μm; C, E, F, and H, 40 μm; D, G, and I, 20 μm.