Volume 12, Number 6—June 2006
Research
Genetic Divergence of Toxoplasma gondii Strains Associated with Ocular Toxoplasmosis, Brazil
Figure 3
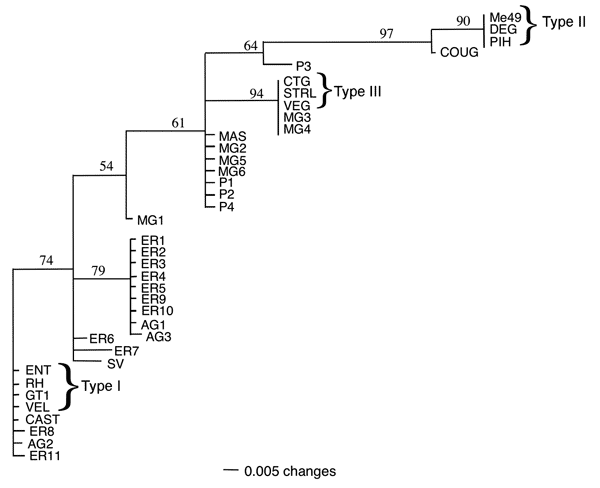
Figure 3. Neighbor-joining phylogram of 38 Toxoplasma gondii strains derived from polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism typing at loci (SAG2, SAG3, GRA6, and BTUB). Distances were calculated according to Nei and Li (21) and the distance matrix analyzed using the phylogenetic analysis program PAUP*4.0b to generate an unrooted phylogram (22). The numbers on the branches indicate the bootstrap values (1,000 replicates). Strain designations are shown in the Table.
References
- Dubey JP, Beattie CP. Toxoplasmosis of animals and man. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press; 1988. p. 220.
- Mead PS, Slutsker L, Dietz V, McCaig LF, Bresee JS, Shapiro C, Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999;5:607–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Moura L, Bahia-Oliveira LMG, Wada MA, Jones JL, Tuboi SH, Carmo EH, Waterborne toxoplasmosis, Brazil, from field to gene. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:326–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bahia-Oliveira LM, Jones JL, Azevedo-Silva J, Alves CC, Orefice F, Addiss DG. Highly endemic, waterborne toxoplasmosis in north Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:55–62.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sibley LD, Boothroyd JC. Virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii comprise a single clonal lineage. Nature. 1992;359:82–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Howe DK, Sibley LD. Toxoplasma gondii comprises three clonal lineages: correlation of parasite genotype with human disease. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:1561–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dardé ML, Bouteille B, Pestre-Alexandre M. Isoenzyme analysis of 35 Toxoplasma gondii isolates and the biological and epidemiological implications. J Parasitol. 1992;78:786–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ajzenberg D, Cogne N, Paris L, Bessieres MH, Thulliez P, Fillisetti D, Genotype of 86 Toxoplasma gondii isolates associated with human congenital toxoplasmosis and correlation with clinical findings. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:684–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ajzenberg D, Bañuls AL, Su C, Dumètre A, Demar M, Carme B, Genetic diversity, clonality and sexuality in Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol. 2004;34:1185–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Silveira C, Belfort R Jr, Muccioli C, Abreu MT, Martins MC, Victora C, A follow-up study of Toxoplasma gondii infection in southern Brazil. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001;131:351–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Glasner PD, Silveira C, Kruszon-Moran D, Martins MC, Burnier M, Silveira S, An unusually high prevalence of ocular toxoplasmosis in southern Brazil. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992;114:136–44.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gilbert RE, Stanford MR. Is ocular toxoplasmosis caused by prenatal or postnatal infection? Br J Ophthalmol. 2000;84:224–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Holland GN. Reconsidering the pathogenesis of ocular toxoplasmosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999;128:502–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Holland GN. Ocular toxoplasmosis: a global reassessment. Part I: epidemiology and course of disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;136:973–88. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vallochi AL, Muccioli C, Martins MC, Silveira C, Belfort R Jr, Rizzo LV. The genotype of Toxoplasma gondii strains causing ocular toxoplasmosis in humans in Brazil. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139:350–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khan A, Su C, German M, Storch GA, Clifford D, Sibley LD. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii strains from immunocompromised patients reveals high prevalence of type I strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:5881–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ferreira AM, Vitor RW, Carneiro ACAV, Brandão GP, Melo MN. Genetic variability of Brazilian Toxoplasma gondii strains detected by random amplified polymorphic DNA-polymerase chain reaction (RAPD-PCR) and simple sequence repeat anchored-PCR (SSR-PCR). Infect Genet Evol. 2004;4:131–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fazaeli A, Carter PE, Dardé ML, Pennington TH. Molecular typing of Toxoplasma gondii strains by GRA6 gene sequence analysis. Int J Parasitol. 2000;30:637–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Su C, Evans D, Cole RH, Kissinger JC, Ajioka JW, Sibley LD. Recent expansion of Toxoplasma through enhanced oral transmission. Science. 2003;299:414–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nei M, Li WH. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979;76:5269–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swofford DL. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (* and other methods). Vol. 4.0b10. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2002.
- Higgins DG, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ. Using CLUSTAL for multiple sequence alignments. Methods Enzymol. 1996;266:382–402. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Frenkel JK. Pathophysiology of toxoplasmosis. Parasitol Today. 1988;4:273–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dupouy-Camet J, de Souza SL, Maslo C, Paugam A, Saimot AG, Benarous R, Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in venous blood from AIDS patients by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;31:1866–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tirard V, Niel G, Rosenheim M, Katlama C, Ciceron L, Ogunkolade W, Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis in patients with AIDS by isolation of the parasite from the blood. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:634. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li WH, Graur D. Fundamentals of molecular evolution. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 1991.
- Neto EC, Anele E, Rubim R, Brites A, Schulte J, Becker D, High prevalence of congenital toxoplasmosis in Brazil estimated in a 3-year prospective neonatal screening study. Int J Epidemiol. 2000;29:941–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Petersen E, Pollak A, Reiter-Owona I. Recent trends in research on congenital toxoplasmosis. Int J Parasitol. 2001;31:115–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Santos CBA, Carvalho ACFB, Ragozo AMA, Soares RM, Amaku M, Yai LEO, First isolation and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from finishing pigs from São Paulo State, Brazil. Vet Parasitol. 2005;131:207–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dubey JP, Graham DH, Blackston CR, Lehmann T, Gennari SM, Ragozo AMA, Biological and genetic characterisation of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from chickens (Gallus domesticus) from São Paulo, Brazil: unexpected findings. Int J Parasitol. 2002;32:99–105. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Silva AV, Pezerico SB, Lima VY, d'Arc Moretti L, Pinheiro JP, Tanaka EM, Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii strains isolated from dogs with neurological signs. Vet Parasitol. 2005;127:23–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dubey JP, Navarro IT, Sreekumar C, Dahl E, Freire RL, Kawabata HH, Toxoplasma gondii infections in cats from Paraná, Brazil: seroprevalence, tissue distribution, and biologic and genetic characterization of isolates. J Parasitol. 2004;90:721–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Grigg ME, Ganatra J, Boothroyd JC, Margolis TP. Unusual abundance of atypical strains associated with human ocular toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 2001;184:633–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Howe DK, Honoré S, Derouin F, Sibley LD. Determination of genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii strains isolated from patients with toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:1411–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dubey JP, Graham DH, da Silva DS, Lehmann T, Bahia-Oliveira LM. Toxoplasma gondii isolates of free-ranging chickens from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: mouse mortality, genotype, and oocyst shedding by cats. J Parasitol. 2003;89:851–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dubey JP, Venturini MC, Venturini L, Piscopo M, Graham DH, Dahl E, Isolation and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from free-ranging chickens from Argentina. J Parasitol. 2003;89:1063–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dubey JP, Gomez-Marin JE, Bedoya A, Lora F, Vianna MC, Hill D, Genetic and biologic characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii isolates in free-range chickens from Colombia, South America. Vet Parasitol. 2005;134:67–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dubey JP, Karhemere S, Dahl E, Sreekumar C, Diabate A, Dabire KR, First biological and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from chickens from Africa (Democratic Republic of Congo, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Kenya). J Parasitol. 2005;91:69–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dubey JP, Graham DH, Dahl E, Hilali M, El-Ghaysh A, Streekumar C, Isolation and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from chickens and ducks from Egypt. Vet Parasitol. 2003;114:89–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: January 04, 2012
Page updated: January 04, 2012
Page reviewed: January 04, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.