Volume 12, Number 8—August 2006
Dispatch
Community-acquired Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Children, Taiwan
Figure
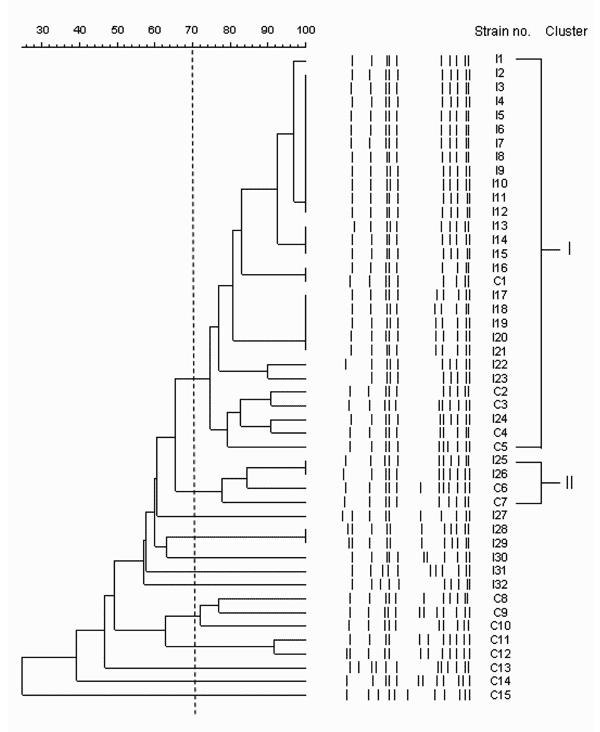
Figure. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns and phylogenetic tree of 47 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates with Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) genes. Banding patterns were digitalized and analyzed with Molecular Analyst Fingerprinting, Fingerprinting Plus, and Fingerprinting DST software (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The grouping method was performed to deduce a dendrogram from the matrix by the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic averages clustering technique after calculation of similarities using the Pearson correlation coefficient between each pair of organisms. The scale indicates the level of pattern similarity. Similarities >70% represent clonal spread of strains. The first letter of each isolate designation indicates the type of the isolate as follows: I, community-acquired MRSA-infecting isolates; C, PVL-positive MRSA-colonizing isolates.