Volume 13, Number 4—April 2007
Dispatch
Human Sapovirus in Clams, Japan
Figure
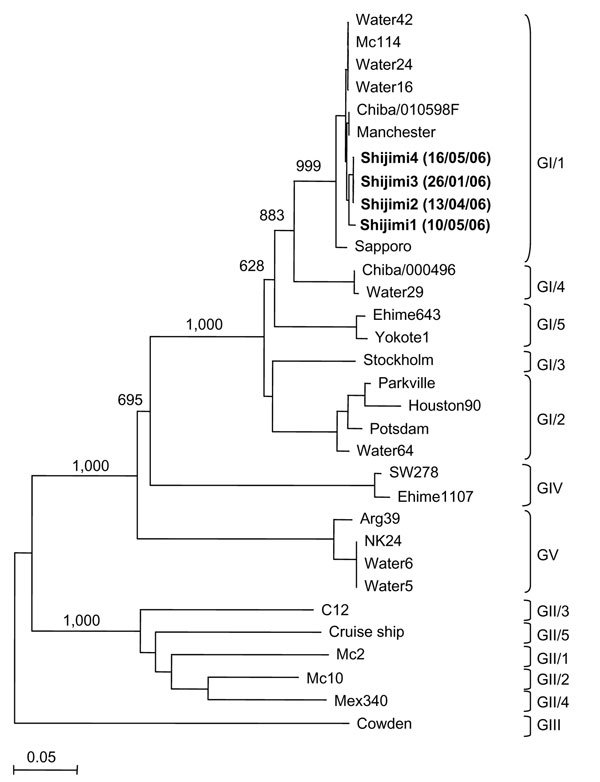
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of sapovirus capsid sequences (≈300 nt) showing the different genogroups and clusters. Numbers on each branch indicate bootstrap values for the genotype. Bootstrap values of ≥950 were considered statistically significant for the grouping. The scale represents nucleotide substitutions per site. GenBank accession nos. for the reference strains are as follows: Arg39, AY289803; C12, AY603425; Chiba/010598F, AJ412825; Chiba000496F, AJ412800; Cruise ship, AY289804; Ehime643, DQ366345; Ehime1107, DQ058829; Houston27, U95644; Manchester, X86560; Mc2, AY237419; Mc10, AY237420; Mex340, AF435812; Parkville, U73124; Cowden, AF182760; Potsdam, AF294739; Sapporo, U65427; Stockholm, AF194182; SW278, DQ125333; water samples, DQ915088–DQ915094; and Yokote, AB253740. Boldface represents sequences detected in this study.