Volume 14, Number 12—December 2008
Research
Sentinel-based Surveillance of Coyotes to Detect Bovine Tuberculosis, Michigan
Figure 3
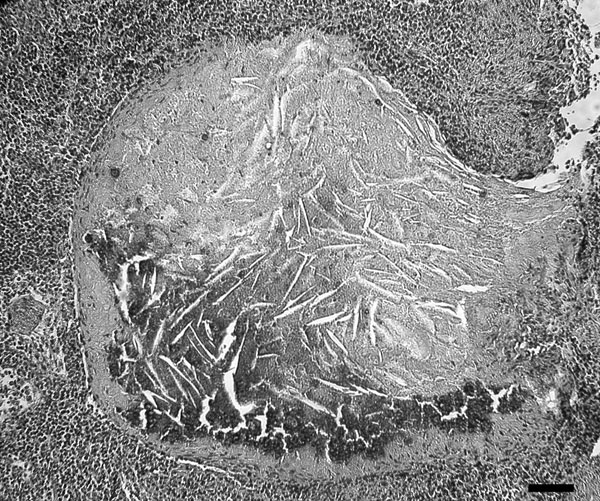
Figure 3. Granulomatous lymphadenitis caused by Mycobacterium bovis in a coyote (Canis latrans). The granulomas consist of a large central necrotic area with mineralization and cholesterol clefts surrounded by a thin rim of primarily macrophages and fibrous connective tissue. Scale bar = 55 μm.
Page created: July 22, 2010
Page updated: July 22, 2010
Page reviewed: July 22, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.