Volume 15, Number 8—August 2009
Dispatch
Epidemiologic Study of Vibrio vulnificus Infections by Using Variable Number Tandem Repeats
Figure 2
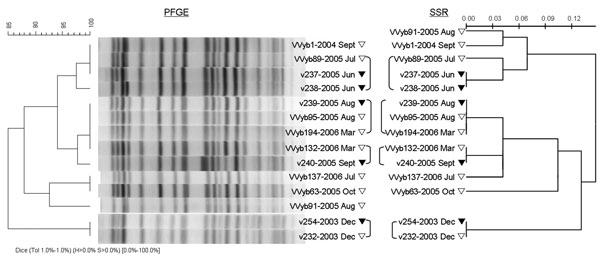
Figure 2. Genetic relationships showing the epidemiologic connection among 12 clinical and environmental Vibrio vulnificus biotype 3 isolates based on pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) analysis compared to analysis at 12 single-sequence repeat (SSR) loci. PFGE profiles were compared by using the Dice coefficient followed by unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean clustering (tolerance, 1.0%). Scale bars represent pattern similarity (% for PFGE and genetic distance for SSR).
Page created: November 01, 2010
Page updated: November 01, 2010
Page reviewed: November 01, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.