Volume 15, Number 8—August 2009
Research
Reproducibility of Serologic Assays for Influenza Virus A (H5N1)
Figure 2
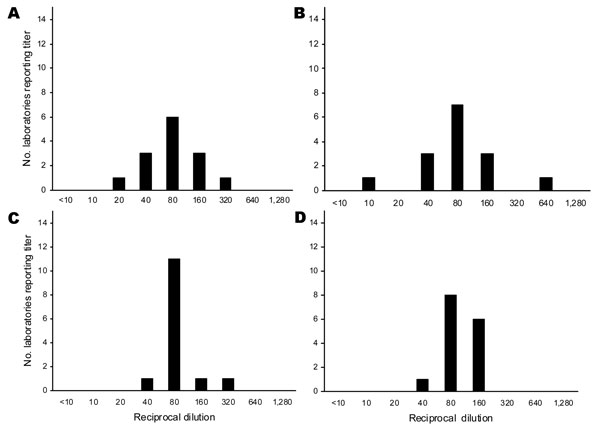
Figure 2. Range of hemagglutination-inhibition (HI) and neutralization titers to clade 1 homologous NIBRG-14 virus in postvaccination serum sample F: the number of laboratories reporting specific titer dilution of absolute titers and titers relative to 07/150. A) Absolute horse HI titers, B) absolute neutralization titers, C) titers relative to 07/150 horse HI titers, D) titers relative to 07/150 neutralization titers.
Page created: November 01, 2010
Page updated: November 01, 2010
Page reviewed: November 01, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.