Volume 17, Number 10—October 2011
Letter
Minority K65R Variants and Early Failure of Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV-1–infected Eritrean Immigrant
Figure
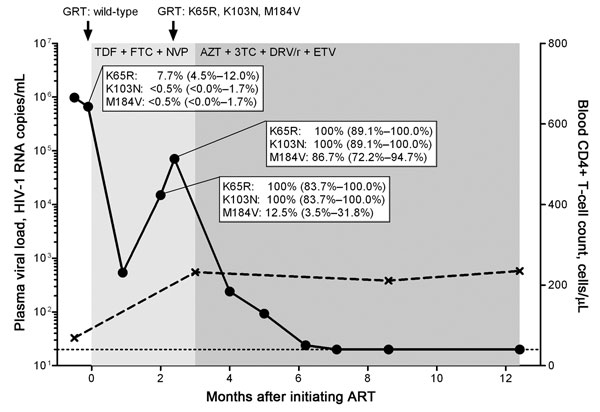
Figure. Kinetics of viremia, CD4+ T-cell count, and drug resistance mutations in a treatment-naive person from Eritrea, infected with HIV-1 subtype C, who was experiencing early antiretroviral therapy (ART) failure. Viral load (circles) was measured by using the Cobas AmpliPrep TaqMan HIV-1 test version 2.0 (Roche Diagnostics, Rotkreuz, Switzerland) with a detection limit of 20 HIV-1 RNA copies/mL plasma (dotted line). CD4+ T-cell count is depicted in crosses. Genotypic resistance testing (GRT) based on population sequencing was performed at time points indicated by black arrows. Duration of different ART regimens is shown in shades of gray. Part of the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (codons 52–218) gene was cloned and sequenced at time points before ART and during virologic failure: n = 222 clones at –2 days before ART, n = 24 clones, and n = 38 clones during virologic failure, respectively. The dynamics of the selection of the K65R, K103N, and M184V mutations are depicted by percentages and 95% confidence intervals. TDF, tenofovir; FTC, emtricitabine; NVP, nevirapine; AZT, zidovudine; 3TC, lamivudine; DRV/r, darunavir in combination with ritonavir; ETV, etravirine.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.