Volume 17, Number 12—December 2011
Dispatch
Novel Sylvatic Rabies Virus Variant in Endangered Golden Palm Civet, Sri Lanka
Figure
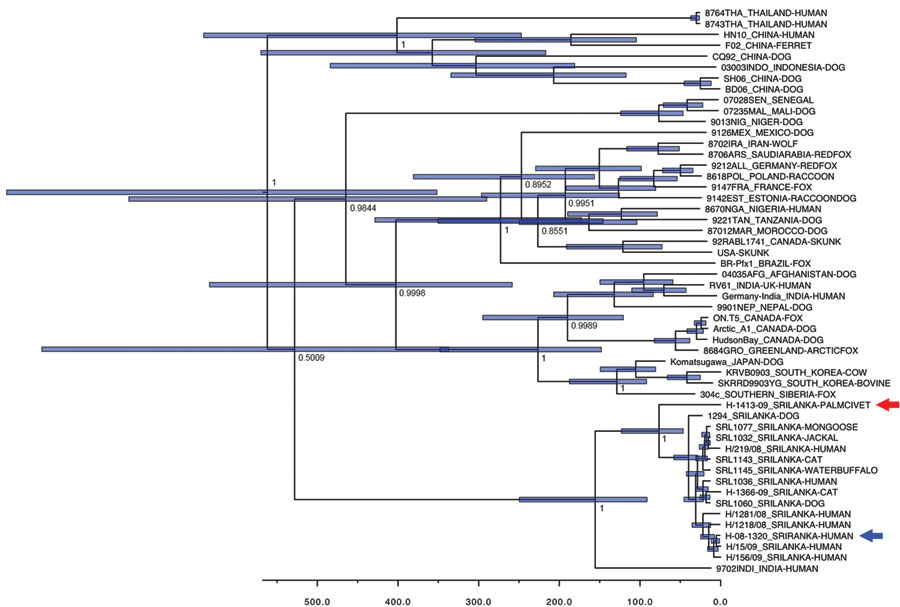
Figure. Bayesian maximum-credibility tree representing the genealogy of rabies virus as obtained by analyzing nucleotide sequences of full N gene sequences (1,350 nt). Nodes correspond to mean age at which lineages are separated from the most recent common ancestor; blue horizontal bars at nodes represent 95% highest posterior density of the most recent common ancestor. Numbers at main nodes represent posterior values. Horizontal axis at bottom represents time scales in years, beginning at 2010. Red arrow indicates strain H-1413-09; blue arrow indicates strain H-08-1320. Nucleotide sequence data for strains from Sri Lanka appear in nucleotide sequence databases of DNA DataBank of Japan, European Molecular Biology Laboratory, and GenBank with accession no. AB635373 (rabies virus strain H-1413-09), AB638767 (strain H-219-08), AB638768 (strain H-1218-08), AB638769 (strain H-1281-08), AB638770 (strain H-15-09), AB638771 (strain H-156–09), AB638772 (strain H-1366-09), and AB636165 (golden palm civet [Paradoxurus zeylonensis] strain H-1413-09).