Volume 17, Number 2—February 2011
Dispatch
New Avian Influenza Virus (H5N1) in Wild Birds, Qinghai, China
Figure 2
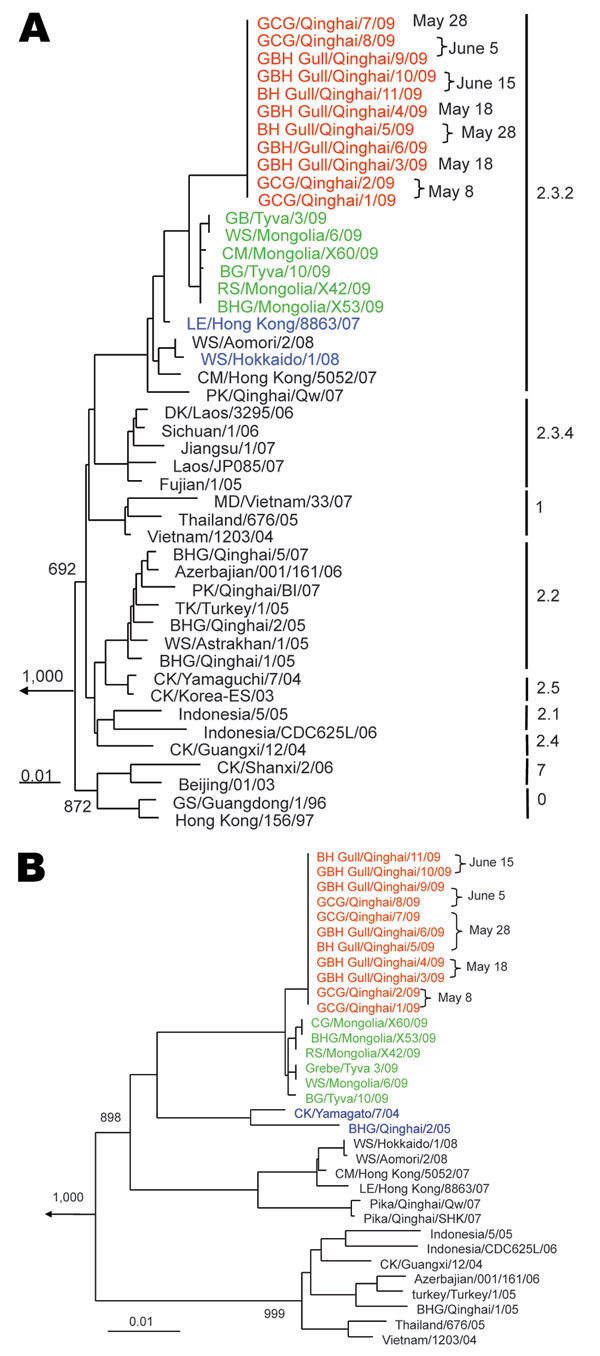
Figure 2. Phylogenetic trees of hemagglutinin genes (nt 29–1,728) (A) and acidic polymerase genes (nt 25–2,151) of avian influenza viruses (H5N1) (B). Clade numbers are indicated on the right in panel A. Trees were constructed by using the PHYLIP program of ClustalX software version 1.81 (www.clustal.org), the neighbor-joining algorithm, and rooted to A/chicken/Pennsylvania/1/83(H5N2). Bootstrap analysis was performed with 1,000 replications. Viruses obtained in this study are shown in red, previously detected viruses that are closely related to avian influenza virus (H5N1) QH09 are shown in blue, and closely related viruses that were detected after the Qinghai wild bird outbreak in 2009 are shown in green. Dates of virus isolation are shown. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site. GCG, great crested grebe; GBH, great black-headed gull; BH, brown-headed gull; GB, grebe; WS, whooper swan; CM, common magpie; BG, bean goose; RS, ruddy shelduck; BHG, bar-headed goose; LE, little egret; PK, pike; DK, duck; MD, Muscovy duck; TK, turkey; CK, chicken; GS, goose; CG, common goldendye.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.