Volume 17, Number 3—March 2011
Dispatch
Phylogeny of European Bat Lyssavirus 1 in Eptesicus isabellinus Bats, Spain
Figure 1
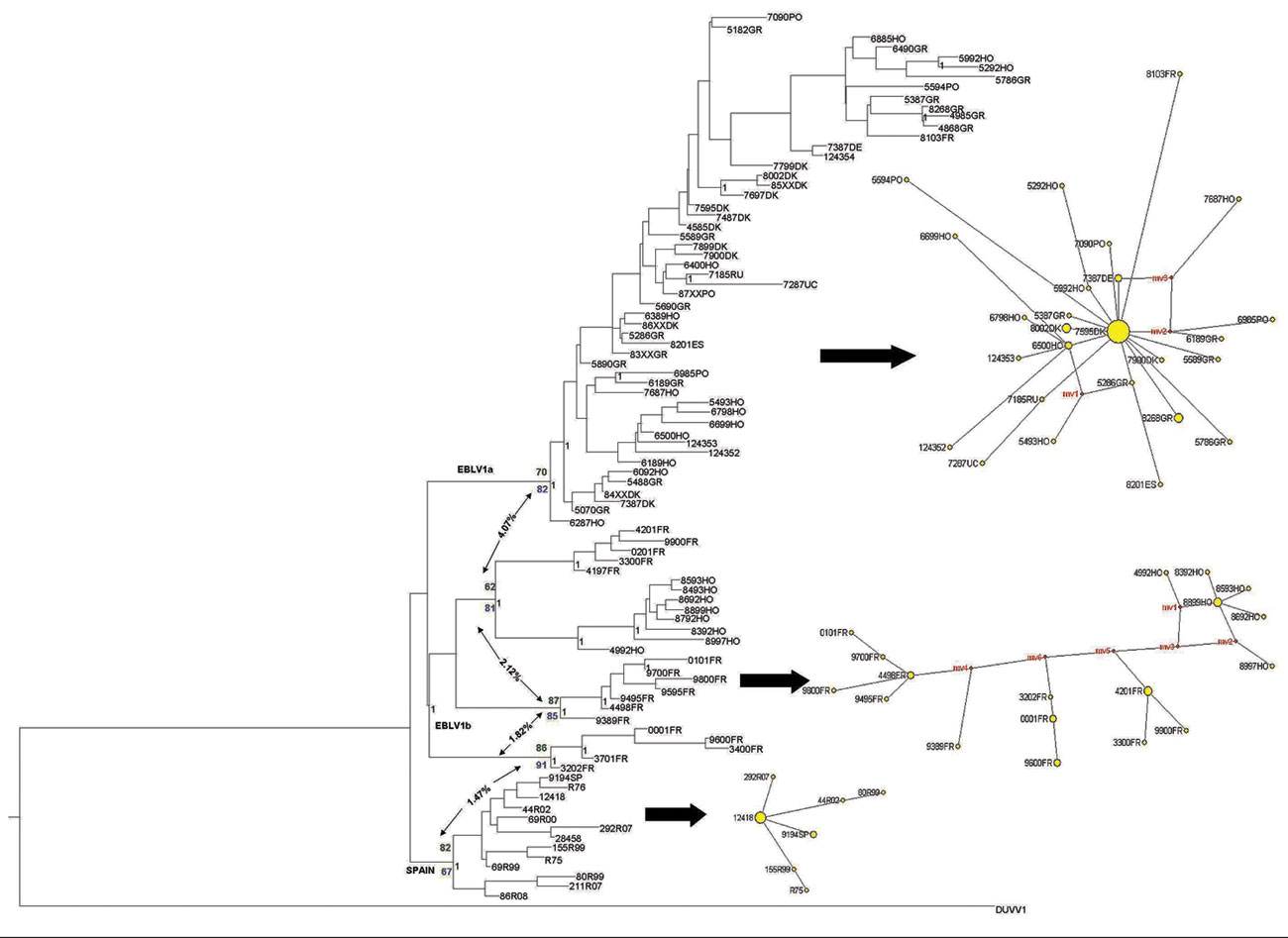
Figure 1. European bat lyssavirus 1 (EBLV-1) phylogenetic reconstruction based on the first 400 bp of the nucleoprotein gene. The tree was obtained by Bayesian inference run for 107 generations; trees were sampled every 100 generations. The first 25% of trees were excluded from the analysis as burn-in. Black numbers indicate posterior probabilities. Bootstrap supports after 1,000 replicates for each node are also shown for maximum-parsimony (green numbers) and maximum-likelihood (blue numbers) analyses. Net p-distance values (as percentages) between groups are indicated by arrows. A parsimony-based network is presented for each major lineage; sizes of yellow circles are proportional to the number of individuals sharing a given haplotype, and reconstructed haplotypes (median vectors) are shown in red. DUVV, Duvenhage virus.