Volume 17, Number 5—May 2011
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Lessons Learned about Pneumonic Plague Diagnosis from 2 Outbreaks, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Figure 2
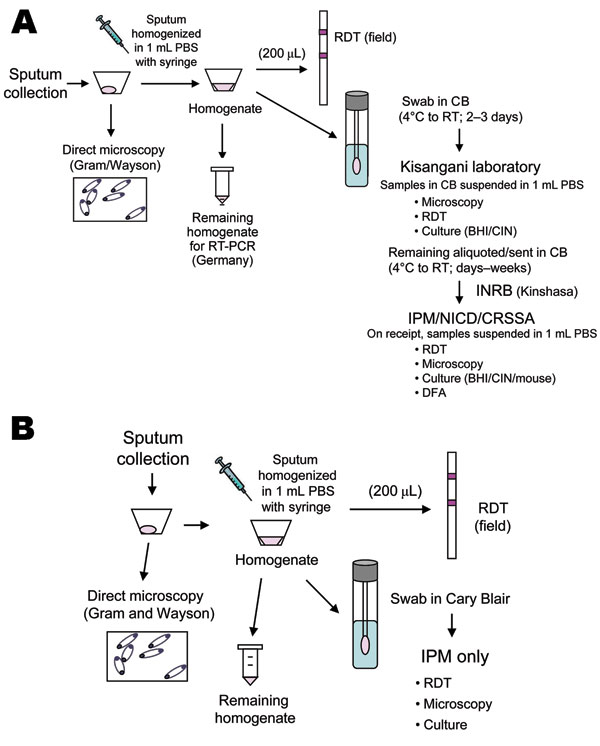
Figure 2. Flow of sample processing for specimens for pneumonic plague outbreaks in Zobia, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), 2005 (A), and Bolebole, DRC, 2006 (B). PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; RDT, rapid diagnostic test; RT, reverse transcription; CB, Cary Blair; BHI/CIN, brain–heart infusion; cefsulodin-Irgasan-novobiocin; INRB, Institut National pour la Recherche Biologique; IPM/NICD/CRSSA, Institut Pasteur de Madagascar/National Institute for Communicable Diseases/Centre de Recherche du Service de Santé des Armées; DFA, direct fluorescent antibody.
Page created: August 14, 2011
Page updated: August 14, 2011
Page reviewed: August 14, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.