Volume 17, Number 7—July 2011
Research
Hansen Disease among Micronesian and Marshallese Persons Living in the United States
Figure 6
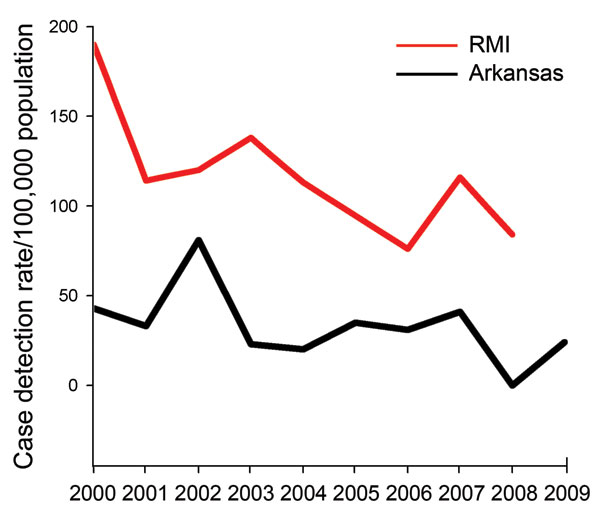
Figure 6. Estimated Hansen disease cases per 100,000 population, Arkansas Marshallese and Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI), 2000–2009. RMI rates from World Health Organization reports (1,2,13); Arkansas cases from National Hansen’s Disease Program records. Arkansas Marshallese population (denominator) derived from US Census estimates (15,17).
References
- World Health Organization. Epidemiological review of leprosy in the Western Pacific Region 2007. Manila, Philippines: World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific; 2007 [cited 2010 Aug 10]. http://www.wpro.who.int/internet/resources.ashx/leprosy/2007_Leprosy_Review.pdf
- World Health Organization. Global leprosy situation, beginning of 2008. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2008;83:293–300.PubMedPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Johnson G. Leprosy outbreak raises concern in Marshall Isles. Pacific Islands Report. 2010 July 30 [cited 2010 Aug 10]. http://pidp.eastwestcenter.org/pireport/2010/July/07-30-04.htm
- National Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy) Program. Data and statistics [cited 2009 Oct 7]. http://www.hrsa.gov/hansens/data.htm
- Ong AKY, Frankel RI, Maruyama MH. Cluster of leprosy cases in Kona, Hawaii; impact of the Compact of Free Association. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1999;67:13–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bomgaars MR, Maruyama M, Tam L. Hansen’s disease in the Pacific (a Hawaiian perspective). Pacific Medical Technology Symposium, Honolulu, Hawaii, August 17–August 20, 1998; p. 153–6 [cited 2009 Oct 7]. http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/PACMED.1998.769893
- Hartzell JD, Zapor M, Peng S, Straight T. Leprosy: A case series and review. South Med J. 2004;97:1252–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weiss MG. Stigma and the social burden of neglected tropical diseases. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2008;2:e237. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- White C. Déjà vu: leprosy and immigration discourse in the twenty-first century United States. Lepr Rev. 2010;81:17–26.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Graham B. Determinants and dynamics of Micronesian emigration. In: Micronesian Voices in Hawai’i Conference, 3–4 April 2008, University of Hawai’i at Manoa [cited 2009 Sep 22]. http://www.hawaii.edu/cpis/2008conf/april2008resources.htm
- Ridley DS, Jopling WH. Classification of leprosy according to immunity—a five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966;34:255–73.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization Expert Committee on Leprosy. Seventh report. WHO technical report series no. 874. Geneva: The Organization; 1998.
- World Health Organization. Overview and epidemiological review of leprosy in the WHO Western Pacific Region 1991–2001. Manila (Philippines): The Organization; 2003 [cited 2009 Sep 22]. http://www.wpro.who.int/publications/pub_9290610573.htm
- Republic of the Marshall Islands Economic Policy, Planning and Statistics Office. Economic situation FY08 and FY09. 2008 [cited 2009 Oct 7]. http://www.spc.int/prism/country/mh/stats/Index.htm
- US Census Bureau. 2005–2007 American Community Survey estimates. 2008 [cited 2009 Oct 7]. http://www.census.gov/acs/www/acs-php/Multi_Year_2005_2007_Data_Profile/index.php
- US Census Bureau. 2008 estimates of Compact of Free Association (COFA) migrants. 2009 [cited 2009 Oct 7]. http://www.uscompact.org/FAS_Enumeration.pdf
- US Census Bureau. Marshallese community pilot survey, northwest Arkansas, USA. Office of Insular Affairs/Census Bureau Statistical Enhancement Program, US Department of the Interior; 2001 [cited 2009 Sep 22]. http://www.pacificweb.org/DOCS/rmi/pdf/Arkansas%20Pilot%20Survey.pdf
- Diletto C, Blanc L. Leprosy chemoprophylaxis in Micronesia. Lepr Rev. 2000;71(Suppl):S21–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Iehsi-Keller E. Implementation of chemoprophylaxis in Pohnpei state, Federated States of Micronesia. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1999;67(Suppl):S14–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tin K. Population screening and chemoprophylaxis for household contacts of leprosy patients in the Republic of the Marshall Islands. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1999;67(Suppl):S26–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Office of Management and Budget. Report to the Congress on the Compacts of Free Association with the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) and the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI) for fiscal year 2006. Washington: The Office; 2007 [cited 2009 Oct 7]. http://uscompact.org/files/index.php?dir=US%20Publications%2FCongressional%20Reports
Page created: August 18, 2011
Page updated: August 18, 2011
Page reviewed: August 18, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.