Volume 17, Number 8—August 2011
Research
Asymptomatic Primary Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection among Adults
Figure 3
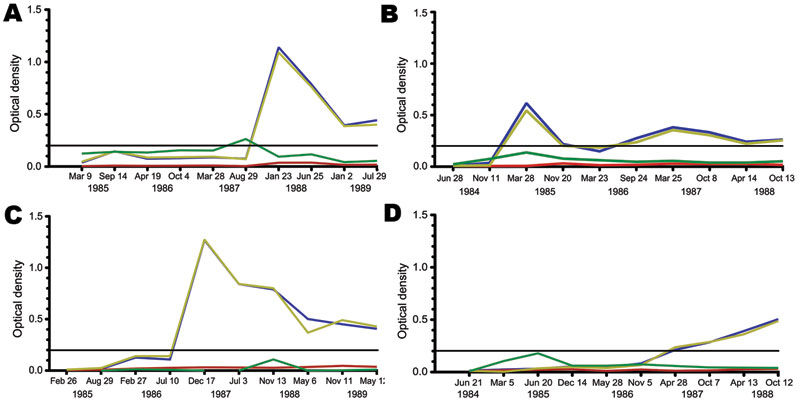
Figure 3. Representative patterns of Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV) seroconversion among participants in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA. Most participants showed MCV immunoglobulin (Ig) M (green line) and IgG (blue line) patterns similar to patient 1 (A) (MCV IgM peak immediately preceding IgG seroconversion) or patient 2 (B) (MCV IgM and IgG are concordant). For patient 3 (C), no IgM peak was detected during MCV IgG seroconversion. Delayed MCV IgG seroconversion, as seen with patient 4 (D), could also occur 1–2 years after an initial IgM spike. The black line represents the 0.2 optical density threshold value for MCV IgG positivity. The specificity of this test is shown by MCV virus-like particle (VLP) competition (red line) and BK virus (BKV) competition (gold line), in which MCV IgG titers are measured after plasma are preincubated with VLP antigen from the respective viruses. MCV IgG reactivity is markedly reduced by MCV competition but not BKV competition.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.