Volume 17, Number 9—September 2011
Dispatch
Bartonella quintana Infections in Captive Monkeys, China
Figure
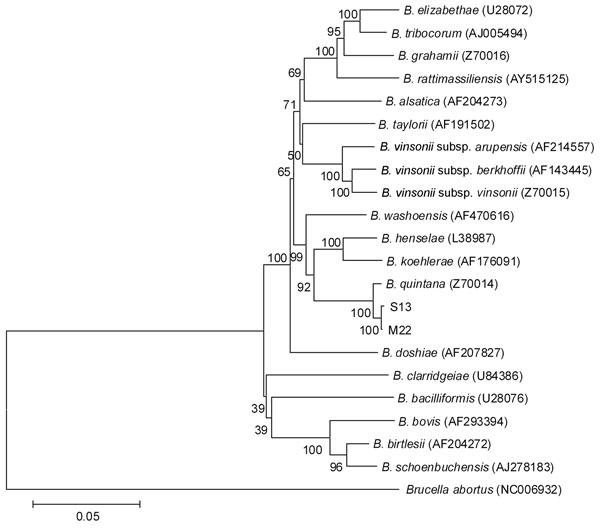
Figure. Phylogenetic dendrogram of Bartonella spp., inferred from alignment of concatenated sequence data (4,007 bp) by using a maximum-likelihood algorithm, within the MEGA4 suite (www.megasoftware.net). The strength of proposed branching orders was tested by bootstrapping (1,000 replicates), and the percentage of samples supporting the proposed branching order are indicated at each node. Sequence data from the 5 loci studied for isolates S13 (from captive 3-year-old female rhesus macaque monkey, China) and M22 (from captive 2-year-old male rhesus macaque monkey, China) were submitted to GenBank under accession nos. HQ014621 (S13 16S rDNA), HQ014622 (S13 ISR), HQ014623 (S13 ftsZ), HQ014624 (S13 gltA), HQ014625 (S13 ribC), HQ014628 (M22 16S rDNA), HQ014629 (M22 ISR), HQ014630 (M22 ftsZ), HQ014627 (M22 gltA), and HQ014626 (M22 ribC). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.