Volume 18, Number 12—December 2012
Dispatch
Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus, Thailand, 2010–2011
Figure 2
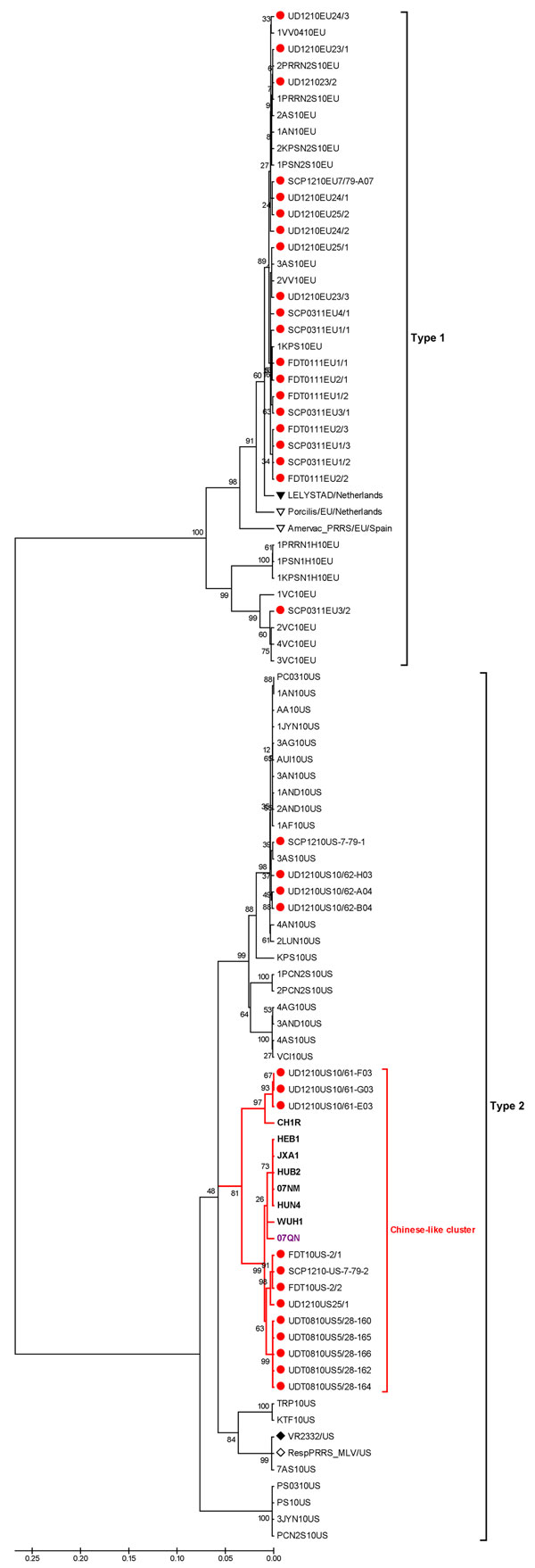
Figure 2. . . Phylogenetic analysis of types 1 and 2 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) isolates constructed by the neighbor-joining method and based on the nucleotide sequences of complete ORF5 genes. The analysis included the following: previous and recent isolates (solid red circles) from herds in Thailand that had an outbreak of HP-PRRSV; European references, including Lelystad virus (solid triangle) and 2 type 1 modified live vaccines (Porcilis PRRS, MSD Animal Health, Boxmeer, the Netherlands; and AMERVAC PRRS, Hipra, Spain) from Europe (open triangles); North American references, including VR2332 (solid diamond) and North American modified live vaccines (Ingelvac PRRS MLV, Boehringer Ingelheim, USA) (open diamonds); modified live vaccines from the People’s Republic of China (CH1R) (open square); isolates from the People’s Republic of China (boldface); and isolate from Vietnam (purple font). Scale bar indicate nucleotide substitutions per site; numbers at nodes represent the percentage of 1,000 bootstrap replicates.