Volume 18, Number 3—March 2012
Letter
Ilheus Virus Infection in Human, Bolivia
Figure
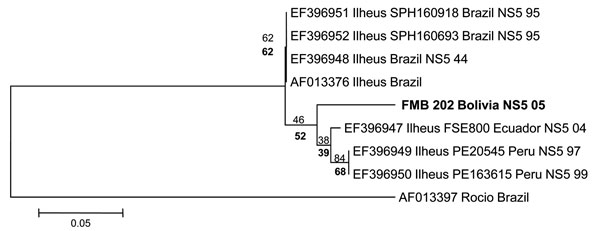
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of the nonstructural protein 5 (NS5) gene region of 7 Ilheus virus isolates and a 189-bp nt sequence (FMB 202 Bolivia). Alignments were analyzed by using the neighbor-joining method with the Kimura 2-parameter algorithm in MEGA5 (www.megasoftware.net). Variation rate among sites was modeled with a gamma distribution (shape parameter = 1). Bootstrap confidence limits (from 1,000 replicates) are indicated at each node. Values in boldface below branches were obtained by parsimony analysis. Boldface indicates virus isolated in this study. Rocio virus (GenBank accession no. AF013397) was included as an outgroup on the basis of the phylogram of Kuno and Chang (10). Sequence generated in our study was deposited in GenBank under accession no. JN679229. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Laemmert HW, Hughes T. The virus of Ilheus encephalitis: isolation, serological specificity and transmission. J Immunol. 1947;55:61–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shope RE. Epidemiology of other arthropod-borne flaviviruses infecting humans. In: Chambers T, Monath T, editors. The flaviviruses: detection, diagnosis and vaccination development. Vol. 61. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic; 2003. p. 386–7.
- Nassar ES, Coimbra TL, Rocco IM, Pereira LE, Ferreira IB, de Souza LT, Human disease caused by an arbovirus closely related to Ilheus virus: report of five cases. Intervirology. 1997;40:247–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Spence L, Anderson CR, Downs WG. Isolation of Ilheus virus from human beings in Trinidad, West Indies. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1962;56:504–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Srihongse S, Johnson CM. Isolation of Ilheus virus from man in Panama. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967;16:516–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Johnson BW, Cruz C, Felices V, Espinoza WR, Manock SR, Guevara C, Ilheus virus isolate from a human, Ecuador. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:956–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Forshey BM, Guevara C, Laguna-Torres VA, Cespedes M, Vargas J, Gianella A, Arboviral etiologies of acute febrile illnesses in Western South America, 2000–2007. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4:e787. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martin DA, Muth D, Brown T, Johnson A, Karabatsos N, Roehrig J. Standardization of immunoglobulin M capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for routine diagnosis of arboviral infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1823–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kuno G, Chang GJ, Tsuchiya KR, Karabatsos N, Cropp CB. Phylogeny of the genus Flavivirus. J Virol. 1998;72:73–83.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kuno G, Chang GJ. Biological transmission of arboviruses: reexamination of and new insights into components, mechanisms, and unique traits as well as their evolutionary trends. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:608–37. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Current affiliation: University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, Texas, USA.