Volume 18, Number 5—May 2012
Dispatch
Coxsackievirus A21, Enterovirus 68, and Acute Respiratory Tract Infection, China
Figure 2
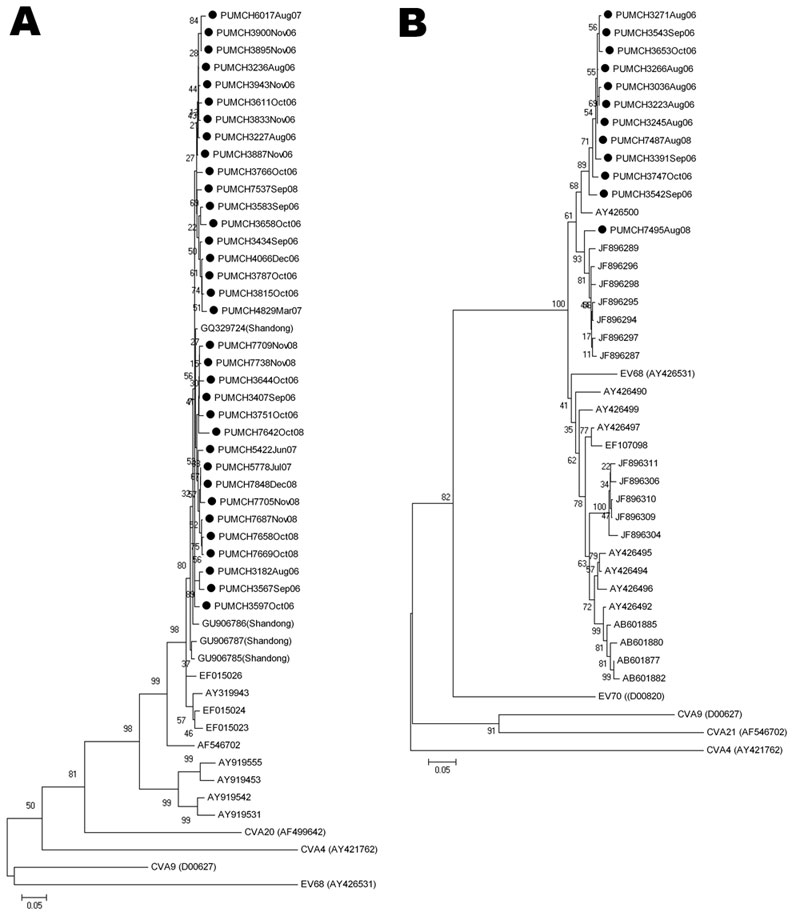
Figure 2. . . Phylogenetic analysis of human enteroviruses according to partial viral protein 1 (VP1) nucleotide sequences. The tree was generated with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Neighbor-joining analysis of the targeted VP1 nucleotide sequence was performed by using the Kimura 2-parameter model with MEGA software version 4.0 (www.megasoftware.net). The scale bars indicate evolutionary distance. GenBank accession numbers for reference serotypes are indicated in parentheses. Each detected strain is indicated by black circles and a specific identification code followed by the patient number and the time of sampling. Strains detected by other research groups are indicated by a GenBank accession number. A) Phylogenetic tree of partial coxsackievirus (CV) A21 VP1 gene. The 375-bp fragments, which correspond to the locations of nt 2565–2939 of the CVA21 prototype strain (GenBank accession no. AF546702), were used to construct the tree. Enterovirus 68 (EV68), CVA9, CVA4, and CVA20 (GenBank accession nos. AY426531, D00627, AY421762, and AF499642, respectively) were used as outgroups. B) Phylogenetic tree of partial EV68 VP1 gene. The 390-bp fragments, which correspond to the locations of nt 2494–2883 of the EV68 prototype strain (GenBank accession no. AY426531), were used to construct the phylogenetic tree. CVA9, CVA4, CVA21, and EV70 (GenBank accession nos. D00627, AY421762, AF546702, and D00820, respectively) were used as outgroups.