Volume 18, Number 9—September 2012
Letter
Henipavirus-related Sequences in Fruit Bat Bushmeat, Republic of Congo
Figure
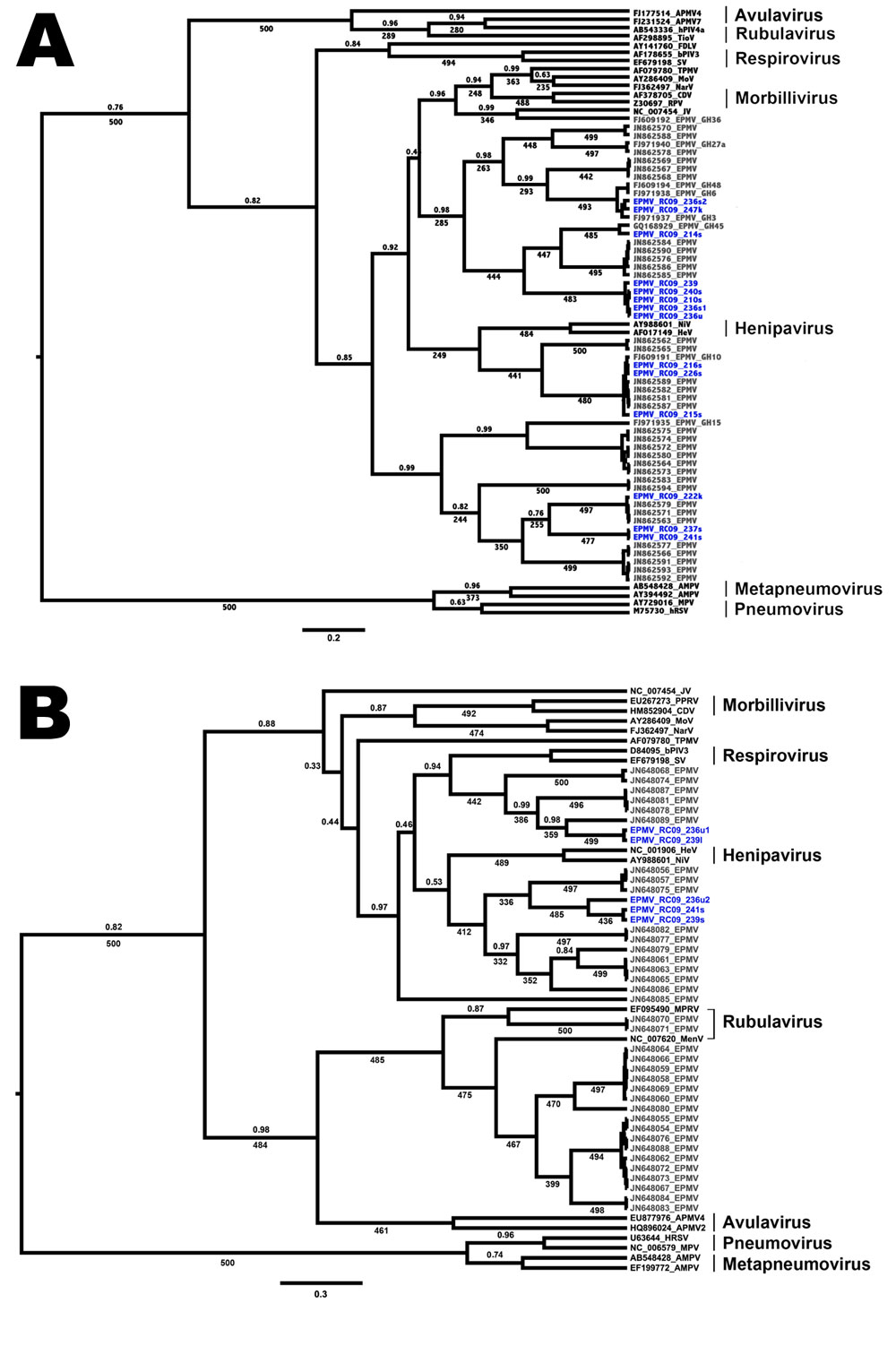
Figure. . Phylogenetic trees showing the placement of Eidolon paramyxovirus (EPMV) sequences in the diversity of Paramyxoviridae, based on partial large gene sequences (384 nt and 474 nt, respectively) of the respirovirus, morbillivirus, and henipavirus fragment (A) and the Paramyxovirinae (PAR) fragment (B), Republic of Congo, 2009. EPMV sequences from Ghana are printed in gray, and novel EPMV sequences from the Republic of Congo are printed in blue. Trees were computed by using BEAST version 1.7.1 (http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Main_Page) under the assumption of a relaxed, uncorrelated lognormal clock and the Yule process speciation model. Values given are posterior probabilities (above branches) and values resulting from nonparametric bootstrapping (below branches; 500 pseudoreplicates) after analysis in PhyML version 3.0 (http://www.atgc-montpellier.fr/phyml/). For better visibility, only posterior probabilities values <1 and bootstrap values >225 (45%) are indicated. Scale bar indicates substitutions per site. For detailed dataset composition and processing, see the Technical Appendix. Novel EPMV sequences are shown in blue and were deposited into GenBank under accession nos. HE647821–HE647839 and HE801055–HE801056. APMV, avian paramyxovirus; AMPV, avian metapneumovirus; bPIV, bovine parainfluenza virus; CDV, canine distemper virus; FDLV, fer-de-lance virus; HeV, Hendra virus; hPIV, human parainfluenza virus; HRSV, human respiratory syncytial virus; JV, J-virus; MenV, Menangle virus; MoV, Mossmann virus; MPRV, Mapuera virus; MPV, murine pneumonia virus; NarV, Nariva virus; NiV, Nipah virus; PPRV, peste-des-petits-ruminants virus; RPV, Rinderpest virus; SV, Sendai virus; TioV, Tioman virus; TPMV, Tupaia paramyxovirus.