Volume 18, Number 9—September 2012
Letter
Rickettsia raoultii–like Bacteria in Dermacentor spp. Ticks, Tibet, China
Figure
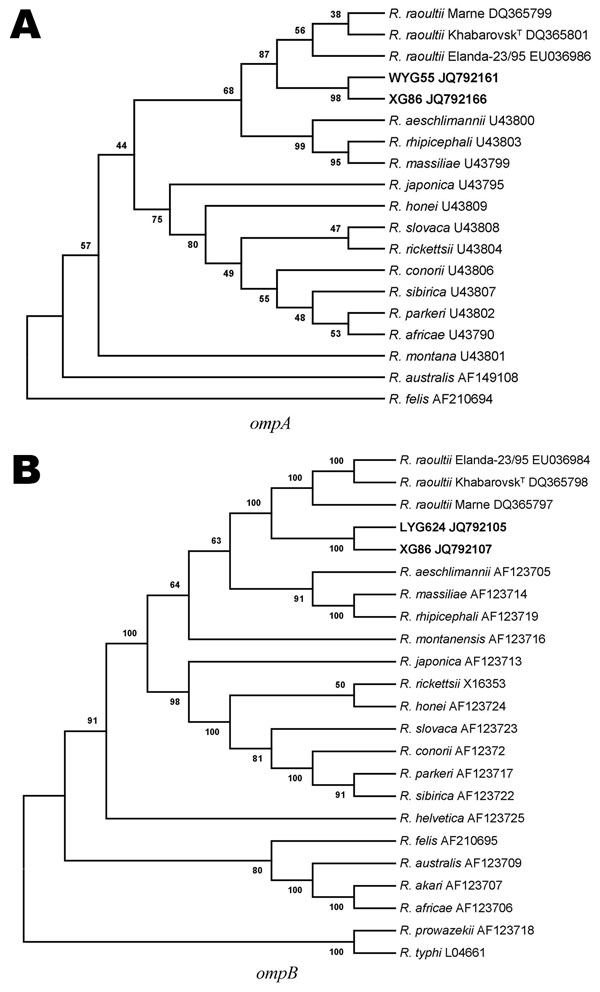
Figure. . . Unrooted phylogenetic trees inferred from comparison of A) outer membrane protein A (ompA) and B) ompB gene sequences of rickettsial species by using the neighbor-joining method. Sequences in boldface were obtained during this study. Numbers at nodes are the proportion of 100 bootstrap resamplings that support the topology shown.
Page created: August 17, 2012
Page updated: August 17, 2012
Page reviewed: August 17, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.