Volume 19, Number 1—January 2013
Letter
Characterization of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus, Eritrea, 2002–2011
Figure
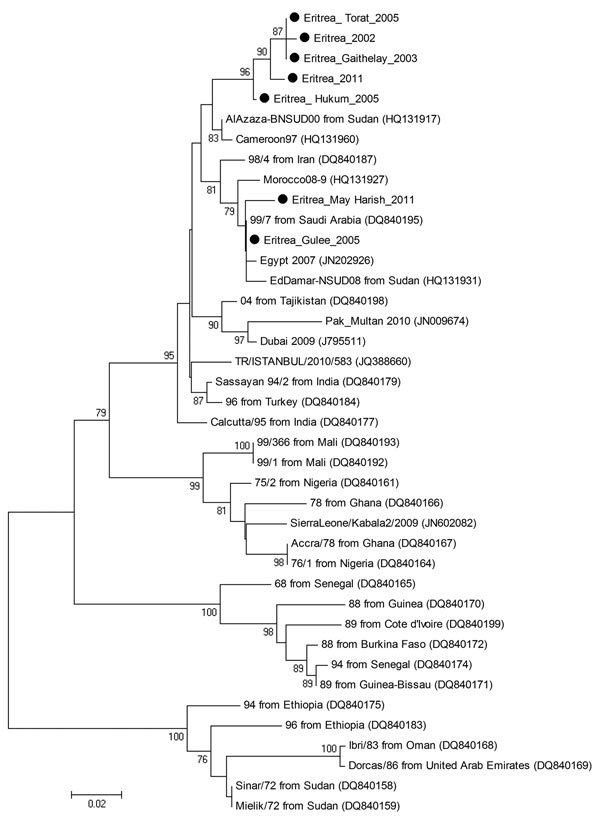
Figure. . Phylogenetic tree showing the genetic relationships between isolates of peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV). The tree was constructed on the basis of 255-nt sequences of the PPRV nucleoprotein gene. Black dots indicate sequences obtained in this study. Lineages are indicated on the right, and GenBank accession numbers are shown in parentheses. Analysis was performed by using the MEGA4 software (6) and neighbor-joining (maximum composite likelihood) methods. Bootstrap support values >70 are shown at nodes (1,000 replicates). The scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Banyard AC, Parida S, Batten C, Oura C, Kwiatek O, Libeau G. Global distribution of peste des petits ruminants virus and prospects for improved diagnosis and control. J Gen Virol. 2010;91:2885–97. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kwiatek O, Ali YH, Saeed IK, Khalafalla AI, Mohamed OI, Obeida AA, Asian lineage of peste des petits ruminants virus, Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1223–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Munir M, Zohari S, Suluku R, Leblanc N, Kanu S, Sankoh FA, Genetic characterization of peste des petits ruminants virus, Sierra Leone. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:193–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Couacy-Hymann E, Roger F, Hurard C, Guillou JP, Libeau G, Diallo A. Rapid and sensitive detection of peste des petits ruminants virus by a polymerase chain reaction assay. J Virol Methods. 2002;100:17–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–8.
- Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 20, 2012
Page updated: December 20, 2012
Page reviewed: December 20, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.