Volume 19, Number 11—November 2013
Research
Pseudorabies Virus Variant in Bartha-K61–Vaccinated Pigs, China, 2012
Figure 2
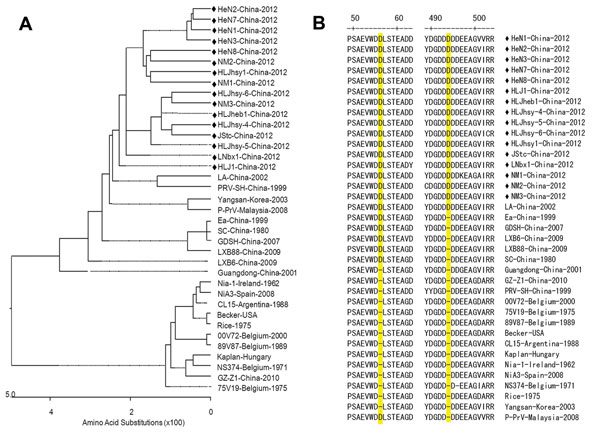
Figure 2. . Phylogenetic analysis and comparison, based on gE amino acid sequences, of pseudorabies virus (PRV) isolates. An unrooted tree was constructed from the aligned amino acid sequences of 39 PRV isolates. Black diamonds indicate 16 PRV isolates from China that were collected in 2012; these isolates belong to a relatively independent branch in the phylogenetic tree (A) and possess 2 aspartic acid (Asp, D) insertions (positions 48 and 492–495), which are highlighted in yellow (B).
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: October 31, 2013
Page updated: October 31, 2013
Page reviewed: October 31, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.