Distinct Lineage of Vesiculovirus from Big Brown Bats, United States
Terry Fei Fan Ng

, Cindy Driscoll, Maria Paz Carlos, Algernon Prioleau, Robert Schmieder, Bhakti Dwivedi, Jakk Wong, Yunhee Cha, Steven Head, Mya Breitbart, and Eric Delwart
Author affiliations: Blood Systems Research Institute, San Francisco, California, USA (T.F.F. Ng, J. Wong, Y. Cha, E. Delwart); University of California, San Francisco (T.F.F. Ng, E. Delwart); University of South Florida, St. Petersburg, Florida, USA (T.F.F. Ng, B. Dwivedi, M. Breitbart); Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Oxford, Maryland, USA (C. Driscoll); Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene, Baltimore, Maryland, USA (M.P. Carlos, A. Prioleau); San Diego State University, San Diego, California, USA (R. Schmieder); The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, California, USA (S. Head)
Main Article
Figure
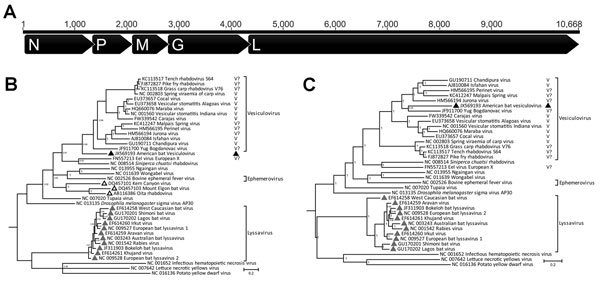
Figure. . . Analyses of American bat vesiculovirus (ABVV) compared with other members of the family Rhabdoviridae. A) Genome organization of ABVV; B) Bayesian inference tree of the ABVV N gene; C) Bayesian inference tree of the 5 concatenated ABVV genes (N, P, M, G, L). For the Bayesian analyses, sequences from the entire gene were used, except for a few partially sequenced genomes for which only ≈100 aa were publicly available. Posterior probabilities (>75%) of the Bayesian analysis are shown next to each node. Formally classified vesiculoviruses are labeled with “V,” whereas potential vesiculoviruses not formally recognized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are labeled with “V?.” Distinct clades of bat rhabdoviruses are labeled with triangles of different colors: black, vesiculovirus; gray, lyssavirus; white, unclassified. N, nucleoprotein; P, phosphoprotein; M, matrix protein; G, glycoprotein; L, polymerase protein. Scale bar indicates amino acid substitutions per site.
Main Article
Page created: November 19, 2013
Page updated: November 19, 2013
Page reviewed: November 19, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
