Volume 19, Number 12—December 2013
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Potential Role of Deer Tick Virus in Powassan Encephalitis Cases in Lyme Disease–endemic Areas of New York, USA
Figure 1
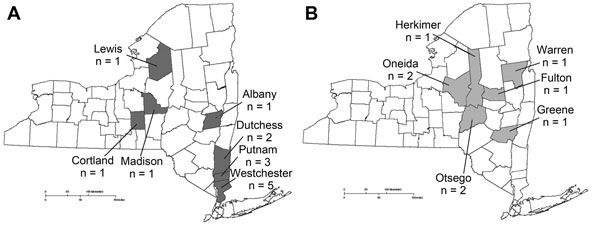
Figure 1. . . Cases of Powassan/deer tick virus encephalitis, by county, New York, USA, for 2004–2012 (A) and 1958–2003 (B) (19). A total of 14 cases occurred during 2004–2012 and 9 cases during 1958–2003. One additional case from 1958–2003 is not shown because the patient had lived in and traveled through multiple counties in the 6 weeks before illness onset (20).
References
- Grard G, Moureau G, Charrel RN, Lemasson JJ, Gonzalez JP, Gallian P, Genetic characterization of tick-borne flaviviruses: new insights into evolution, pathogenetic determinants and taxonomy. Virology. 2007;361:80–92 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McLean DM, Donohue WL. Powassan virus: isolation of virus from a fatal case of encephalitis. Can Med Assoc J. 1959;80:708–11 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Leonova GN, Kondratov IG, Ternovoi VA, Romanova EV, Protopopova EV, Chausov EV, Characterization of Powassan viruses from Far Eastern Russia. Arch Virol. 2009;154:811–20 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kuno G, Artsob H, Karabatsos N, Tsuchiya KR, Chang GJ. Genomic sequencing of deer tick virus and phylogeny of Powassan-related viruses of North America. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;65:671–6 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pesko KN, Torres-Perez F, Hjelle BL, Ebel GD. Molecular epidemiology of Powassan virus in North America. J Gen Virol. 2010;91:2698–705 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Johnson DK, Staples JE, Sotir MJ, Warshauer DM, Davis JP. Tickborne Powassan virus infections among Wisconsin residents. WMJ. 2010;109:91–7 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Telford SR III, Armstrong PM, Katavolos P, Foppa I, Garcia AS, Wilson ML, A new tick-borne encephalitis-like virus infecting New England deer ticks, Ixodes dammini. Emerg Infect Dis. 1997;3:165–70 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ebel GD, Campbell EN, Goethert HK, Spielman A, Telford SR III. Enzootic transmission of deer tick virus in New England and Wisconsin sites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;63:36–42 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gholam BI, Puksa S, Provias JP. Powassan encephalitis: a case report with neuropathology and literature review. CMAJ. 1999;161:1419–22 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tavakoli NP, Wang H, Dupuis M, Hull R, Ebel GD, Gilmore EJ, Fatal case of deer tick virus encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2099–107 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- El Khoury MY, Hull RC, Bryant PW, Escuyer KL, St George K, Wong SJ, Diagnosis of acute deer tick virus encephalitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56:e40–7 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Neitzel DF, Lynfield R, Smith K. Powassan virus encephalitis, Minnesota, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:686 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hinten SR, Beckett GA, Gensheimer KF, Pritchard E, Courtney TM, Sears SD, Increased recognition of Powassan encephalitis in the United States, 1999–2005. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2008;8:733–40 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hicar MD, Edwards K, Bloch K. Powassan virus infection presenting as acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in Tennessee. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30:86–8 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sung S, Wurcel AG, Whittier S, Kulas K, Kramer LD, Flam R, Powassan meningoencephalitis, New York, New York, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1504–6 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2012 Nationally notifiable diseases and conditions and current case definitions. Atlanta: The Centers; 2012 [cited 2013 Oct 24]. http://wwwn.cdc.gov/nndss/document/2012_Case%20Definitions.pdf
- Wong SJ, Demarest VL, Boyle RH, Wang T, Ledizet M, Kar K, Detection of human anti-flavivirus antibodies with a West Nile virus recombinant antigen microsphere immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:65–72 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wong SJ, Boyle RH, Demarest VL, Woodmansee AN, Kramer LD, Li H, Immunoassay targeting nonstructural protein 5 to differentiate West Nile virus infection from Dengue and St. Louis encephalitis virus infections and from flavivirus vaccination. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:4217–23 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Artsob H. Powassan encephalitis. In: Monath TP, editor. The arboviruses: epidemiology and ecology. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press, Inc.; 1989. p. 29–49.
- Embil JA, Camfield P, Artsob H, Chase DP. Powassan virus encephalitis resembling herpes simplex encephalitis. Arch Intern Med. 1983;143:341–3 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dupuis M, Hull R, Wang H, Nattanmai S, Glasheen B, Fusco H, Molecular detection of viral causes of encephalitis and meningitis in New York State. J Med Virol. 2011;83:2172–81 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Deibel R, Srihongse S, Woodall JP. Arboviruses in New York State: an attempt to determine the role of arboviruses in patients with viral encephalitis and meningitis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979;28:577–82 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of Powassan encephalitis—Maine and Vermont, 1999–2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50:761–4 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile virus disease and other arboviral diseases—United States, 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011;60:1009–13 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Birge J, Sonnesyn S. Powassan virus encephalitis, Minnesota, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:1669–71 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raval M, Singhal M, Guerrero D, Alonto A. Powassan virus infection: case series and literature review from a single institution. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5:594 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Falco RC, Fish D. Ticks parasitizing humans in a Lyme disease endemic area of southern New York State. Am J Epidemiol. 1988;128:1146–52 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tokarz R, Jain K, Bennett A, Briese T, Lipkin WI. Assessment of polymicrobial infections in ticks in New York State. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010;10:217–21 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ebel GD, Kramer LD. Short report: duration of tick attachment required for transmission of Powassan virus by deer ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;71:268–71 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Anderson JF, Armstrong PM. Prevalence and genetic characterization of Powassan virus strains infecting Ixodes scapularis in Connecticut. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;87:754–9 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ebel GD, Foppa I, Spielman A, Telford SR III. A focus of deer tick virus transmission in the northcentral United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999;5:570–4 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brackney DE, Nofchissey RA, Fitzpatrick KA, Brown IK, Ebel GD. Stable prevalence of Powassan virus in Ixodes scapularis in a northern Wisconsin focus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;79:971–3 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Costero A, Grayson MA. Experimental transmission of Powassan virus (Flaviviridae) by Ixodes scapularis ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1996;55:536–46 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dupuis AP II, Peters RJ, Prusinski MA, Falco RC, Ostfeld RS, Kramer LD. Isolation of deer tick virus (Powassan virus, lineage II) from Ixodes scapularis and detection of antibody in vertebrate hosts sampled in the Hudson Valley, New York State. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:185.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ryder JW, Pinger RR, Glancy T. Inability of Ixodes cookei and Amblyomma americanum nymphs (Acari: Ixodidae) to transmit Borrelia burgdorferi. J Med Entomol. 1992;29:525–30 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tunkel AR, Glaser CA, Bloch KC, Sejvar JJ, Marra CM, Roos KL, The management of encephalitis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:303–27 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Portolani M, Pietrosemoli P, Meacci M, Sabbatini AM, Pecorari M, Mantovani G, Detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid from immunocompetent individuals with brain disorders. New Microbiol. 1998;21:77–9 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tyler KL. Update on herpes simplex encephalitis. Rev Neurol Dis. 2004;1:169–78 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: December 11, 2013
Page updated: December 11, 2013
Page reviewed: December 11, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.