Volume 19, Number 5—May 2013
Letter
Search for Possible Additional Reservoirs for Human Q Fever, the Netherlands
Figure
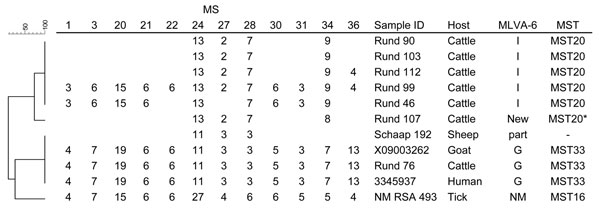
Figure. . Phylogenetic tree of the genotypes of Coxiella burnetii from the samples of this study based on multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analyses (MLVA) including 12 loci (MLVA-12). Repeats per locus are shown, and open spots indicate missing values. MLVA-6 are results of the analysis with 6 MLVA loci (3). MST are results of the analysis with multispacer sequence typing (MST) (5). MLVA 6 loca (MLVA-6) and MST revealed full genotypes unless stated otherwise. Two strains representing the outbreak genotype of C. burnetii (X09003262, 3345937) in the Netherlands and the Nine Mile (NM) RSA 493 are included as reference. MS, mini satellite; G and I, MLVA-6 genotypes of C. burnetii as published (3,7); MSTxx, MST genotypes as published (5). *Based on partial genotype; part, partial genotype. – (in MST column) indicates no results obtained. Scale bar indicates percentage similarity.
References
- Roest HI, Tilburg JJ, van der Hoek W, Vellema P, van Zijderveld FG, Klaassen CH, The Q fever epidemic in the Netherlands: history, onset, response and reflection. Epidemiol Infect. 2011;139:1–12 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roest HI, Ruuls RC, Tilburg JJ, Nabuurs-Franssen MH, Klaassen CH, Vellema P, Molecular epidemiology of Coxiella burnetii from ruminants in Q fever outbreak, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:668–75 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tilburg JJ, Rossen JW, van Hannen EJ, Melchers WJ, Hermans MH, van de Bovenkamp J, Genotypic diversity of Coxiella burnetii in the 2007–2010 Q fever outbreak episodes in the Netherlands. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:1076–8 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Arricau-Bouvery N, Hauck Y, Bejaoui A, Frangoulidis D, Bodier CC, Souriau A, Molecular characterization of Coxiella burnetii isolates by infrequent restriction site-PCR and MLVA typing. BMC Microbiol. 2006;6:38 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tilburg JJ, Roest HJ, Buffet S, Nabuurs-Franssen MH, Horrevorts AM, Raoult D, Epidemic genotype of Coxiella burnetii among goats, sheep, and humans in the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:887–9 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dijkstra F, van der Hoek W, Wijers N, Schimmer B, Rietveld A, Wijkmans CJ, The 2007–2010 Q fever epidemic in the Netherlands: characteristics of notified acute Q fever patients and the association with dairy goat farming. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012;64:3–12 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tilburg JJ, Roest HJ, Nabuurs-Franssen MH, Horrevorts AM, Klaassen CH. Genotyping reveals the presence of a predominant genotype of Coxiella burnetii in consumer milk products. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:2156–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Karagiannis I, Schimmer B, Van Lier A, Timen A, Schneeberger P, Van Rotterdam B, Investigation of a Q fever outbreak in a rural area of the Netherlands. Epidemiol Infect. 2009;137:1283–94 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar