Volume 19, Number 6—June 2013
Dispatch
Novel SARS-like Betacoronaviruses in Bats, China, 2011
Figure 2
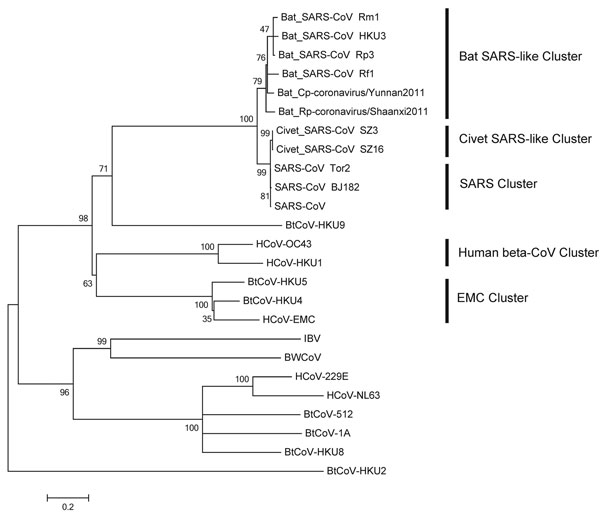
Figure 2. . Phylogenetic tree of novel betacoronaviruses based on the deduced amino acid sequence of spike protein. SARS, severe acute respiratory syndrome; CoV, coronavirus; HCoV, human CoV; BtCoV, bat CoV; BWCoV, beluga whale CoV; IBV, avian infectious bronchitis. Scale bar indicates genetic distance estimated by using WAG+G+I+F model implemented in MEGA5 (www.megasoftware.net).
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: May 20, 2013
Page updated: May 20, 2013
Page reviewed: May 20, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.