Volume 19, Number 7—July 2013
Dispatch
Avian Metapneumovirus Subgroup C Infection in Chickens, China
Figure 1
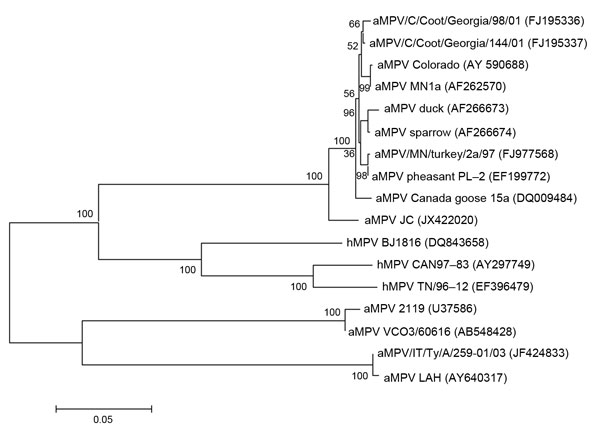
Figure 1. . . Genetic relatedness between the matrix (M) protein gene of members of avian metapneumoviruses (aMPV) and human metapneumovirus (hMPV). Phylogenetic tree was constructed on the basis of the neighbor-joining clustering method by using MEGA 5.10 software (www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap values (based on 500 replicates) are indicated at each branching point. Reference strains obtained from GenBank are indicated. The M sequence of the isolate JC used in the phylogenetic analysis has been deposited in GenBank under accession no. JX422020. Scale bar indicates estimated phylogenetic divergence.
Page created: May 24, 2013
Page updated: June 17, 2013
Page reviewed: June 17, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.