Volume 19, Number 7—July 2013
Letter
Novel Bat-borne Hantavirus, Vietnam
Figure
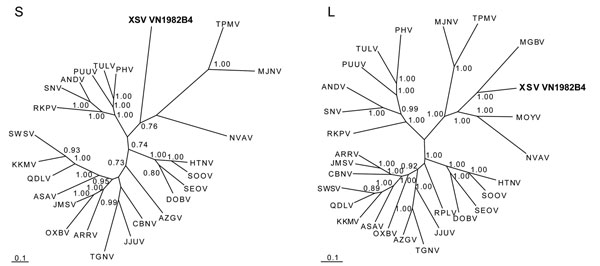
Figure. . Phylogenetic trees, based on 499-nt and 4,582-nt regions of the small (S) and large (L) genomic segments, respectively, of Xuan Son virus (XSV VN1982B4) (GenBank accession nos. S: KC688335, L: JX912953), generated by the maximum-likelihood and Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo estimation methods, under the GTR+I+Γ model of evolution. Because tree topologies were similar when RAxML and MrBayes were used, the tree generated by MrBayes was displayed. The phylogenetic position of XSV is shown in relation to chiropteran-borne hantaviruses, Mouyassué virus ([MOYV] JQ287716) from the banana pipistrelle and Magboi virus ([MGBV] JN037851) from the hairy slit-faced bat. The taxonomic identity of the XSV-infected Pomona roundleaf bat was confirmed by mitochondrial DNA analysis (GenBank accession no. JX912954). The numbers at each node are Bayesian posterior probabilities (>0.7), and the scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site. Boldface indicates the Xuan Son virus detected in Pomona roundleaf bat, Vietnam. Representative soricomorph-borne hantaviruses include Thottapalayam virus ([TPMV] AY526097, EU001330) from the Asian house shrew; Imjin virus ([MJNV] EF641804, EF641806) from the Ussuri white-toothed shrew; Jeju virus ([JJUV] HQ663933, HQ663935) from the Asian lesser white-toothed shrew; Tanganya virus ([TGNV] EF050455, EF050454) from the Therese’s shrew; Azagny virus ([AZGV] JF276226, JF276228) from the West African pygmy shrew; Cao Bang virus ([CBNV] EF543524, EF543525) from the Chinese mole shrew; Ash River virus ([ARRV] EF650086, EF619961) from the masked shrew; Jemez Springs virus ([JMSV] FJ593499, FJ593501) from the dusky shrew; Seewis virus ([SWSV] EF636024, EF636026) from the Eurasian common shrew; Kenkeme virus ([KKMV] GQ306148, GQ306150) from the flat-skulled shrew; Qiandao Lake virus ([QDLV] GU566023, GU566021) from the stripe-backed shrew; Camp Ripley virus ([RPLV] EF540771) from the northern short-tailed shrew; Asama virus ([ASAV] EU929072, EU929078) from the Japanese shrew mole; Oxbow virus ([OXBV] FJ539166, FJ593497) from the American shrew mole; Rockport virus ([RKPV] HM015223, HM015221) from the eastern mole; and Nova virus ([NVAV] FJ539168, FJ593498) from the European common mole. Also shown are representative rodent-borne hantaviruses, including Hantaan virus ([HTNV] NC_005218, NC_005222), Soochong virus ([SOOV] AY675349, DQ562292), Dobrava-Belgrade virus ([DOBV] NC_005233, NC_005235), Seoul virus ([SEOV] NC_005236, NC_005238), Tula virus ([TULV] NC_005227, NC_005226), Puumala virus ([PUUV] NC_005224, NC_005225), Prospect Hill virus ([PHV] Z49098, EF646763), Andes virus ([ANDV] NC_003466, NC_003468), and Sin Nombre virus ([SNV] NC_005216, NC_005217).