Volume 19, Number 8—August 2013
Letter
Asian Musk Shrew as a Reservoir of Rat Hepatitis E Virus, China
Figure
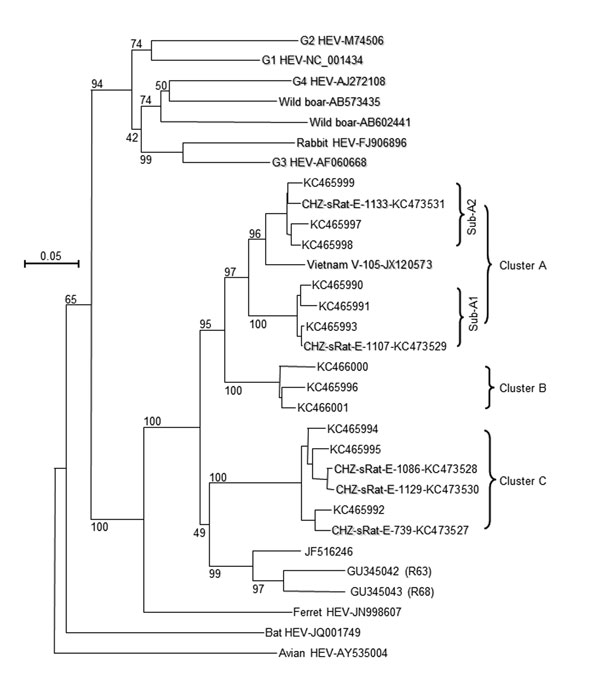
Figure. . . Phylogenetic analysis of rat hepatitis E virus (HEV) isolated from Asian musk shrews (Suncus murinus) in Zhanjiang City, China. Nucleic acid sequence alignment was performed by using ClustalX 1.81 (www.clustal.org). The genetic distance was calculated by using the Kimura 2-parameter method. The phylogenetic tree, with 1,000 bootstrap replicates, was generated by the neighbor-joining method based on the partial sequence (281 nt) of HEV open reading frame 1 of genotype 1–4, wild boar, rabbit, ferret, bat, avian, and rat HEV isolates. The scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
Page created: July 12, 2013
Page updated: July 12, 2013
Page reviewed: July 12, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.