Volume 20, Number 2—February 2014
Dispatch
Genetic Characterization of Coronaviruses from Domestic Ferrets, Japan
Figure 2
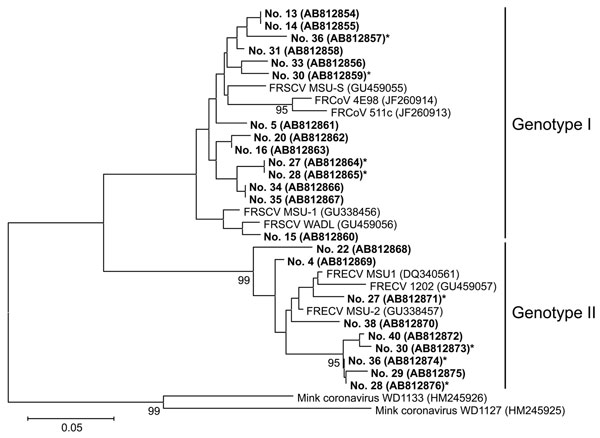
Figure 2. . Phylogenetic tree based on the nucleotide sequences of partial S genes of ferret coronaviruses (FRCoVs) isolated in Japan (shown in boldface; sample IDs are indicated) compared with other coronaviruses (CoVs). The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method in MEGA5.0 software (10); bootstrap values of >90 are shown. Asterisks indicate samples from ferrets infected with FRCoVs of both genotypes1 and 2. DDBJ/EMBL-Bank/GenBank accession numbers for the nucleotide sequences are shown in parentheses. FRSCV, ferret systemic coronavirus; FRECV, ferret enteric coronavirus. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Williams BH, Kiupel M, West KH, Raymond JT, Grant CK, Glickman LT. Coronavirus-associated epizootic catarrhal enteritis in ferrets. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2000;217:526–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wise AG, Kiupel M, Maes RK. Molecular characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with epizootic catarrhal enteritis (ECE) in ferrets. Virology. 2006;349:164–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Garner MM, Ramsell K, Morera N, Juan-Sallés C, Jiménez J, Ardiaca M, Clinicopathologic features of a systemic coronavirus-associated disease resembling feline infectious peritonitis in the domestic ferret (Mustela putorius). Vet Pathol. 2008;45:236–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martínez J, Ramis AJ, Reinacher M, Perpiñán D. Detection of feline infectious peritonitis virus–like antigen in ferrets. Vet Rec. 2006;158:523. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wise AG, Kiupel M, Garner MM, Clark AK, Maes RK. Comparative sequence analysis of the distal one-third of the genomes of a systemic and an enteric ferret coronavirus. Virus Res. 2010;149:42–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Graham E, Lamm C, Denk D, Stidworthy MF, Carrasco DC, Kubiak M. Systemic coronavirus-associated disease resembling feline infectious peritonitis in ferrets in the UK. Vet Rec. 2012;171:200–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martínez J, Reinacher M, Perpiñán D, Ramis A. Identification of group 1 coronavirus antigen in multisystemic granulomatous lesions in ferrets (Mustela putorius furo). J Comp Pathol. 2008;138:54–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Michimae Y, Mikami S, Okimoto K, Toyosawa K, Matsumoto I, Kouchi M, The first case of feline infectious peritonitis–like pyogranuloma in a ferret infected by coronavirus in Japan. J Toxicol Pathol. 2010;23:99–101. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Poon LL, Chu DK, Chan KH, Wong OK, Ellis TM, Leung YH, Identification of a novel coronavirus in bats. J Virol. 2005;79:2001–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Provacia LB, Smits SL, Martina BE, Raj VS, Doel PV, Amerongen GV, Enteric coronavirus in ferrets, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1570–1 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pedersen NC, Liu H, Dodd KA, Pesavento PA. Significance of coronavirus mutants in feces and diseased tissues of cats suffering from feline infectious peritonitis. Viruses. 2009;1:166–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chang HW, de Groot RJ, Egberink HF, Rottier PJ. Feline infectious peritonitis: insights into feline coronavirus pathobiogenesis and epidemiology based on genetic analysis of the viral 3c gene. J Gen Virol. 2010;91:415–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pedersen NC. A review of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection: 1963–2008. J Feline Med Surg. 2009;11:225–58. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chang HW, Egberink HF, Halpin R, Spiro DJ, Rottier PJ. Spike protein fusion peptide and feline coronavirus virulence. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:1089–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: January 17, 2014
Page updated: January 17, 2014
Page reviewed: January 17, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.