Volume 20, Number 2—February 2014
Dispatch
Co-circulation of West Nile Virus Variants, Arizona, USA, 2010
Figure 2
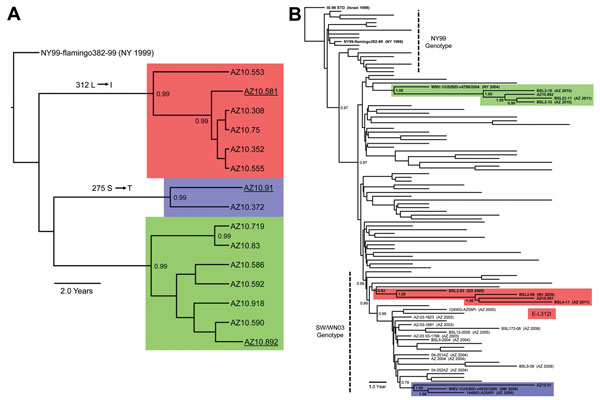
Figure 2. . A) Bayesian phylogenetic tree of envelopes genes of all described Arizona, USA, 2010 isolates of West Nile virus (WNV) (n = 15). Isolates grouped in 3 distinct monophyletic clusters designated A (red), B (blue), and C (green). B) Bayesian phylogenetic tree of full-length encoded open reading frame for 3 Arizona, USA, 2010 isolates: AZ10.581 (red), AZ10.892 (green), AZ10.91 (blue), and 100 representative North American WNV isolates. All applied relaxed clock Bayesian methods used the generalized time reversible + invariant sites + Γ4 substitution model with a lognormal molecular clock and triplicate 50 million state runs produced in BEAST v1.6.2 (3). Inferred phylogenetic trees were edited in FigTree v1.3.1 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/). Consistent phylogenetic topologies with additional neighbor-joining and maximum-likelihood methods further validated these inferred relationships. Posterior probabilities ≥0.90 are indicated for highlighted nodes. Scale bars indicate divergence time in years.
References
- Gibney KB, Colborn J, Baty S, Bunko Patterson AM, Sylvester T, Briggs G, Modifiable risk factors for West Nile virus infection during an outbreak, Arizona, 2010. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;86:895–901. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Godsey MS Jr, Burkhalter K, Young G, Delorey M, Smith K, Townsend J, Entomologic investigations during an outbreak of West Nile virus disease in Maricopa County, Arizona, 2010. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;87:1125–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drummond AJ, Rambaut A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol. 2007;7:214. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Añez G, Grinev A, Chancey C, Ball C, Akolkar N, Land KJ, Evolutionary dynamics of West Nile virus in the United States, 1999–2011: phylogeny, selection pressure and evolutionary time-scale analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2245. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bakonyi T, Hubalek Z, Rudolf I, Nowotny N. Novel flavivirus or new lineage of West Nile virus, central Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:225–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li L, Barrett AD, Beasley DW. Differential expression of domain III neutralizing epitopes on the envelope proteins of West Nile virus strains. Virology. 2005;335:99–105. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McMullen AR, Albayrak H, May FJ, Davis CT, Beasley DW, Barrett AD. Molecular evolution of lineage 2 West Nile virus. J Gen Virol. 2013;94:318–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Papa A, Bakonyi T, Xanthopoulou K, Vazquez A, Tenorio A, Nowotny N. Genetic characterization of West Nile virus lineage 2, Greece, 2010. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:920–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bakonyi T, Ivanics E, Erdelyi K, Ursu K, Ferenczi E, Weissenbock H, Lineage 1 and 2 strains of encephalitic West Nile virus, central Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:618–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McMullen AR, May FJ, Li L, Guzman H, Bueno R Jr, Dennett JA, Evolution of new genotype of West Nile virus in North America. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:785–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhang S, Bovshik EI, Maillard R, Gromowski GD, Volk DE, Schein CH, Role of BC loop residues in structure, function and antigenicity of the West Nile virus envelope protein receptor-binding domain III. Virology. 2010;403:85–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brault AC. Changing patterns of West Nile virus transmission: altered vector competence and host susceptibility. Vet Res. 2009;40:43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Beasley DW, Davis CT, Guzman H, Vanlandingham DL, Travassos da Rosa AP, Parsons RE, Limited evolution of West Nile virus has occurred during its southwesterly spread in the United States. Virology. 2003;309:190–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mann BR, McMullen AR, Guzman H, Tesh RB, Barrett AD. Dynamic transmission of West Nile virus across the United States–Mexican border. Virology. 2013;436:75–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Duggal NK, D’Anton M, Xiang J, Seiferth R, Day J, Nasci R, Sequence analyses of 2012 west nile virus isolates from Texas fail to associate viral genetic factors with outbreak magnitude. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013;89:205–10 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.