Volume 20, Number 5—May 2014
Letter
Serologic Evidence of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus Infection in Northern Sea Otters
Figure
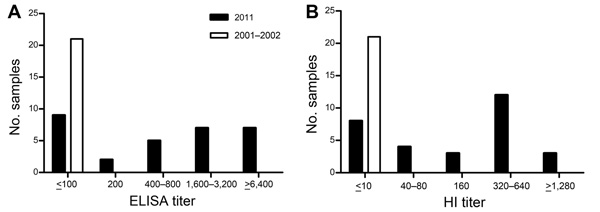
Figure. Results of ELISA and hemagglutination inhibition (HI) testing for influenza viruses in serum samples from northern sea otters captured off the coast of Washington, USA, during studies conducted in August 2011 (n = 30) and 2001–2002 (n = 21)A) IgG for influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 strain A/Texas/05/2009 detected by using standard indirect ELISA techniques with HRP-Protein A (Sigma, StLouis, MO, USA)The ELISA titer was read as the reciprocal of the highest dilution of serum with an OD450nm of >0.2 and 2-fold higher than the OD450nm of control wells lacking serumB) HI for influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 strain A/Mexico/4108/2009HI titers were determined by using 0.5% turkey red blood cells (RBCs) for influenza A(H1N1)pdm09, seasonal influenza A(H1N1), influenza (H3N2), and influenza B viruses that circulated in North America during 2000–2011 and by using 1% horse RBCs supplemented with 0.5% BSA for avian influenza A(H1N1) virus strain A/duck/New York/96HI assay was performed as described (www.who.int/influenza/gisrs_laboratory/manual_diagnosis_surveillance_influenza/en)OD, optical density.