Volume 20, Number 6—June 2014
Dispatch
Identification of Possible Virulence Marker from Campylobacter jejuni Isolates
Figure 1
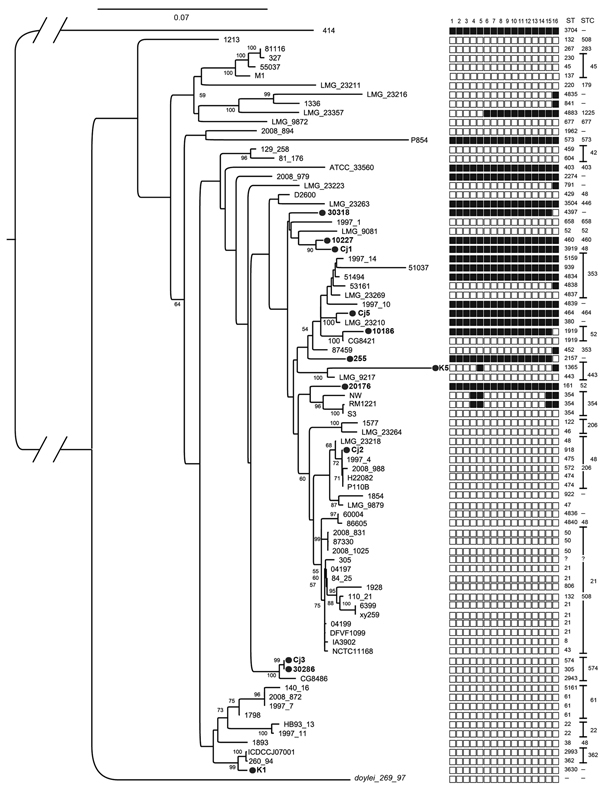
Figure 1. Distribution of the type-six secretion system (T6SS) marker across the phylogenetic diversity of Campylobacter jejuni strains, as determined by multilocus sequence analysisWe generated a maximum-likelihood tree from concatenated nucleotide alignments of 31 housekeeping genes; nucleotide sequences were aligned by using MUSCLE (www.drive5.com/muscle) and masked by using GBLOCKS (http://molevol.cmima.csic.es/castresana/Gblocks.html)Maximum-likelihood analysis was done by using the GTR model in PhyML (http://code.google.com/p/phyml/)Numbers on nodes denote bootstrap values (1,000 bootstrap replicates); values <50 are not shownBlack circles indicate strains whose genomes were sequenced in this study (GenBank accession nosAUUQ00000000, AUUP00000000, AUUO00000000, AUUN00000000, AUUM00000000, AUUL00000000, AUUK00000000, AUUJ00000000, AUUI00000000, ARWS00000000, AUUH00000000, AUUG00000000)We inferred the presence/absence of each of the T6SS genes on the basis of TBLASTN (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastn&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch) searches against the predicted proteins sequences from Cjejuni strain 414 (National Center for Biotechnology Information reference sequence noNZ_CM000855)Presence or absence of each gene is indicated by a black or white square, respectively, for each strain: column 1, hcp; column 2, icmF_1; column 3, icmF_2; column 4, vasK; column 5, FHA; column 6, vasF; column 7, vasE; column 8, vasD; column 9, impA; column 10, impD; column 11, impC; columns 12 and 13, conserved hypotheticals; column 14, vasA; column 15, vasB; column 16, vgrgThe sequence type (ST) and ST complex (STC) columns represent global multilocus sequence types as described by the Oxford multilocus sequence typing scheme (http://pubmlst.org)?, unknown ST; –, isolate could not be allocated to a specific ST or STCFurther details of the isolates are provided in Technical Appendix Table 2.