Volume 21, Number 10—October 2015
Synopsis
Characteristics and Factors Associated with Death among Patients Hospitalized for Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, South Korea, 2013
Figure 1
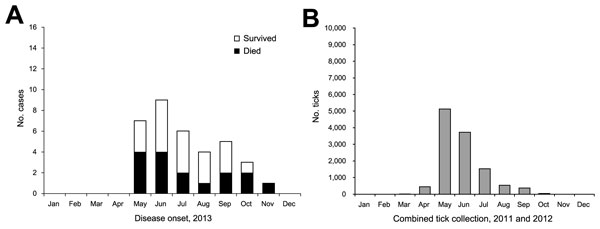
Figure 1. Comparison of epidemic curve for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome cases identified during 2013 and the number of Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks collected per month during 2011 and 2012, South Korea. A) Number of cases of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, by month of onset. B) Combined number of H. longicornis ticks collected, by month (6).
References
- Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1523–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Park SW, Han MG, Yun SM, Park C, Lee WJ, Ryou J. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, South Korea, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1880–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bao CJ, Guo XL, Qi X, Hu JL, Zhou MH, Varma JK, A family cluster of infections by a newly recognized bunyavirus in eastern China, 2007: further evidence of person-to-person transmission. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:1208–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gai Z, Liang M, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Jin C, Wang SW, Person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus through blood contact. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:249–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liu S, Chai C, Wang C, Am S, Lv H, He H, Systematic review of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: virology, epidemiology, and clinical characteristics. Rev Med Virol. 2014;24:90–102. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Park SW, Song BG, Shin EH, Yun SM, Han MG, Park MY, Prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;5:975–7.
- Kim KH, Yi J, Kim G, Choi SJ, Jun KI, Kim NH, Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1892–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yun SM, Lee WG, Ryou J, Yang SC, Park SW, Roh JY, Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks collected from humans, South Korea, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1358–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ko S, Kang JG, Kim SY, Kim HC, Klein TA, Chong ST, Prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in ticks from southern Korea. J Vet Sci. 2010;11:197–203. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yun SM, Song BG, Choi W, Park WI, Kim SY, Roh JY, Prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in ixodid ticks collected from the Republic of Korea during 2011–2012. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2012;3:213–21.
- Yano Y, Shiraishi S, Uchida TA. Effects of temperature on development and growth in the tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Exp Appl Acarol. 1987;3:73–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chung YS, Yoon MB. Interpretation of recent temperature and precipitation trends observed in Korea. Theor Appl Climatol. 2000;67:171–80. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Ding F, Zhang W, Wang L, Hu W, Soares Magalhaes RJ, Sun H, Epidemiologic features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011–2012. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56:1682–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Takahashi T, Maeda K, Suzuki T, Ishido A, Shigeoka T, Tominaga T, The first identification and retrospective study of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Japan. J Infect Dis. 2014;209:816–27. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liu W, Lu QB, Cui N, Li H, Wang LY, Liu K, Case-fatality ratio and effectiveness of ribavirin therapy among hospitalized patients in China who had severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1292–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sun Y, Jin C, Zhan F, Wang X, Liang M, Zhang Q, Host cytokine storm is associated with disease severity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J Infect Dis. 2012;206:1085–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhang YZ, He YW, Dai YA, Xiong Y, Zheng H, Zhou DJ, Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel Bunyavirus in China: pathogenesis and correlates of fatal outcome. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:527–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tang X, Wu W, Wang H, Du Y, Liu L, Kang K, Human-to-human transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus through contact with infectious blood. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:736–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gai ZT, Zhang Y, Liang MF, Jin C, Zhang S, Zhu CB, Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. J Infect Dis. 2012;206:1095–102. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Deng B, Zhou B, Zhang S, Zhu Y, Han L, Geng Y, Clinical features and factors associated with severity and fatality among patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus infection in northeast China. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e80802 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: September 22, 2015
Page updated: September 22, 2015
Page reviewed: September 22, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.