Volume 21, Number 10—October 2015
Research
Effect of Live Poultry Market Closure on Avian Influenza A(H7N9) Virus Activity in Guangzhou, China, 2014
Figure 3
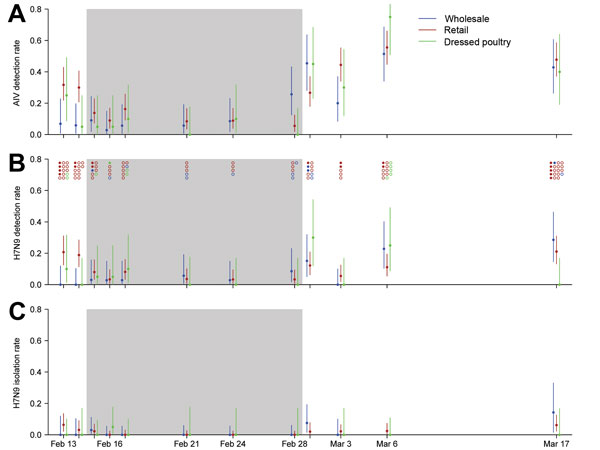
Figure 3. Avian influenza virus (AIV) activity in wholesale, retail, and dressed poultry markets under enhanced surveillance in Guangzhou, China, 2014. A) AIV and B) influenza A(H7N9) virus detection rates as determined by real-time reverse transcription PCR (rRT-PCR). Circles at the top of panel B indicate H7N9 virus–positive (solid) and –negative (open) samples isolated by culture from the different types of poultry markets. Some H7N9 virus samples positive by rRT-PCR did not have sufficient sample remaining for virus culture; the numbers of samples cultured and positive at each time point are shown. C) H7N9 virus isolation rates as determined by culture. Rates for positive cultures were estimated on the basis of the samples available for culture, as described in Materials and Methods. Vertical bars indicate 95% CIs for detection rates and 95% credible intervals for isolation rates. Gray shading indicates the 2-week citywide market closure, which began on February 15, 2014.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.