Volume 21, Number 9—September 2015
Letter
Bifidobacterium breve Sepsis in Child with High-Risk Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Figure
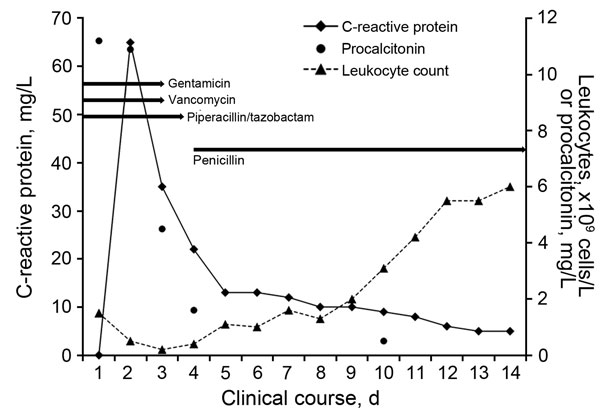
Figure. Schematic presentation of leukocyte count, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin serum levels in clinical course of Bifidobacterium breve sepsis. Arrows indicate the name and duration of each antimicrobial drug treatment.
CrossRef reports the volume should be "13" not "13(" in reference 2 "Bottacini, Ventura, van Sinderen, O’Connell Motherway M., 2014".
Medline reports the volume should be "13" not "13(" in reference 2 "Bottacini, Ventura, van Sinderen, O’Connell Motherway M., 2014".
Page created: August 14, 2015
Page updated: August 14, 2015
Page reviewed: August 14, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.