Volume 21, Number 9—September 2015
Letter
Fatal Accelerated Cirrhosis after Imported HEV Genotype 4 Infection
Figure
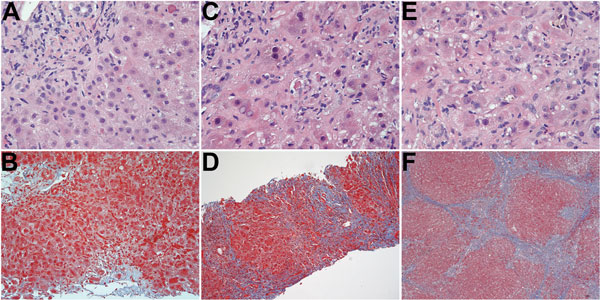
Figure. Serial histologic changes in liver of the patient who received a diagnosis of hepatitis E after a visit to Hong Kong in 2013 (A and B: at first biopsy; C and D: second biopsy; E and F: third biopsy. A) Mild mixed portal infiltration; minimal lobular inflammation; acidophil body present at upper right; and bile duct showing injury with lymphocytic infiltration (original magnification ×400). B) Mild portal inflammation; some interface activity; and portal tracts not showing increased fibrosity (original magnification ×200). C) Mononuclear infiltration of portal tract at upper right with bile duct/ductular infiltration and injury; lobular changes more severe, showing more inflammation, acidophil bodies and reactive nuclear change in hepatocytes with ballooning of some hepatocytes (original magnification ×400). D) Portal and lobular inflammation; and marked increase in fibrosis with bridging and regenerative nodule formation (original magnification ×100). E) Extensive lobular inflammation and reactive hepatocytic changes with nuclear enlargement, prominent nucleoli, and ballooning (original magnification ×400). F) Well-developed cirrhosis (original magnification ×40). Hematoxylin and eosin staining (A, C, E); Masson trichrome staining. (B, D, F).