Volume 22, Number 11—November 2016
CME ACTIVITY - Research
Multidrug-Resistant Corynebacterium striatum Associated with Increased Use of Parenteral Antimicrobial Drugs
Figure 2
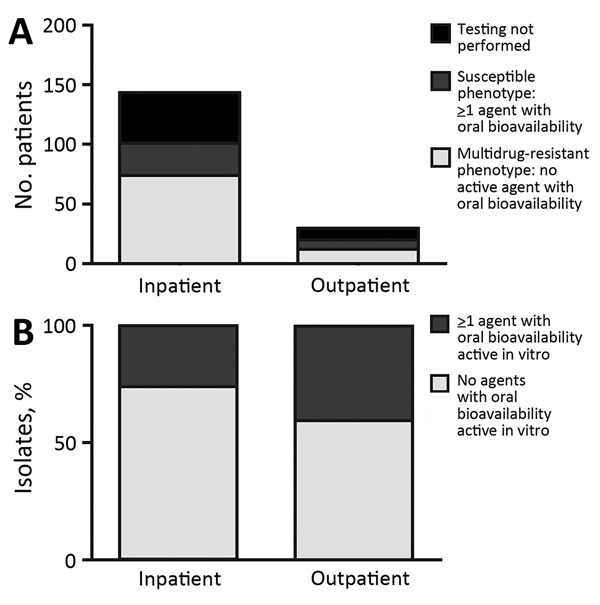
Figure 2. Numbers (A) and percentages (B) of Corynebacterium striatum isolates from patients at the University of Washington Medical Center, Seattle, Washington, USA, 2005–2014, with a multidrug-resistant phenotype for all antimicrobial drugs tested (penicillin, ciprofloxacin, clindamycin, erythromycin, and tetracycline). Inpatient or outpatient indicates clinical setting in which cultures were performed.
1Current affiliation: University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California, USA.
Page created: October 12, 2016
Page updated: October 17, 2016
Page reviewed: October 17, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.