Volume 22, Number 11—November 2016
Research
Immune Responses to Invasive Group B Streptococcal Disease in Adults
Figure 1
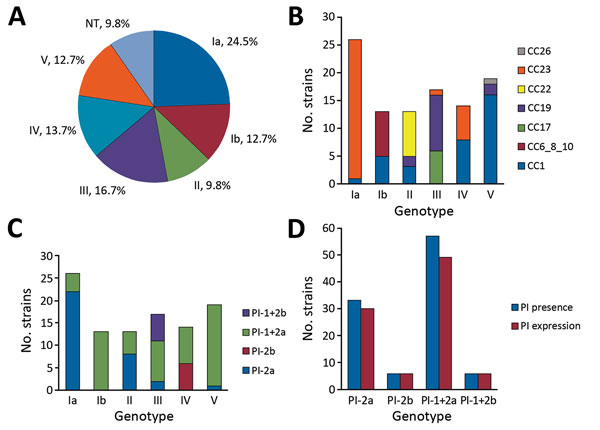
Figure 1. CPS type and PI distribution and expression in 102 group B Streptococcus isolates from adults with invasive infection, Houston, Texas, USA. A) CPS distribution of isolates by capillary precipitin method and latex agglutination assay (indicating CPS expression). B) Correlation between CC distribution and CPS genotype by PCR. C) PI and CPS distribution by genotype. D) Relationship between pilus genotype distribution and pilus expression in isolates expressing >1 pilus type on their surface. CC, clonal complex; CPS, capsular polysaccharide; NT, nontypeable; PI, pilus island.
Page created: October 18, 2016
Page updated: October 18, 2016
Page reviewed: October 18, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.