Novel Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Viruses in Migratory Birds, China, 2013–2014
Li-Chen Zhou
1, Jing Liu
1, En-Le Pei
1, Wen-Jie Xue
1, Jia-Min Lyu, Yin-Ting Cai, Di Wu, Wei Wu, Yu-Yi Liu, Hui-Yu Jin, Yu-Wei Gao, Zheng-Huan Wang

, and Tian-Hou Wang

Author affiliations: Laboratory of Wildlife Epidemic Diseases, Shanghai Key Laboratory for Urban Ecological Processes and Eco-Restoration, School of Life Sciences, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China (L.-C. Zhou, J. Liu, J.-M. Lyu, Z.-H. Wang, T.-H. Wang); Shanghai Municipal Agency of Wildlife Conservation, Shanghai (E.-L. Pei, D. Wu, H.-Y. Jin); Chongming Dongtan National Nature Reserve, Shanghai (W.-J. Xue, W. Wu); Jiuduansha Wetland National Nature Reserve, Shanghai, China (Y.-T. Cai) Wildlife Conservation Section, Shanghai Municipal Forestry Bureau, Shanghai (Y.-Y. Liu); Research Center of Wildlife Disease, Key Laboratory of Jilin Province for Zoonosis Prevention and Control, Military Veterinary Research Institute of Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Changchun, China (Y.-W. Gao)
Main Article
Figure
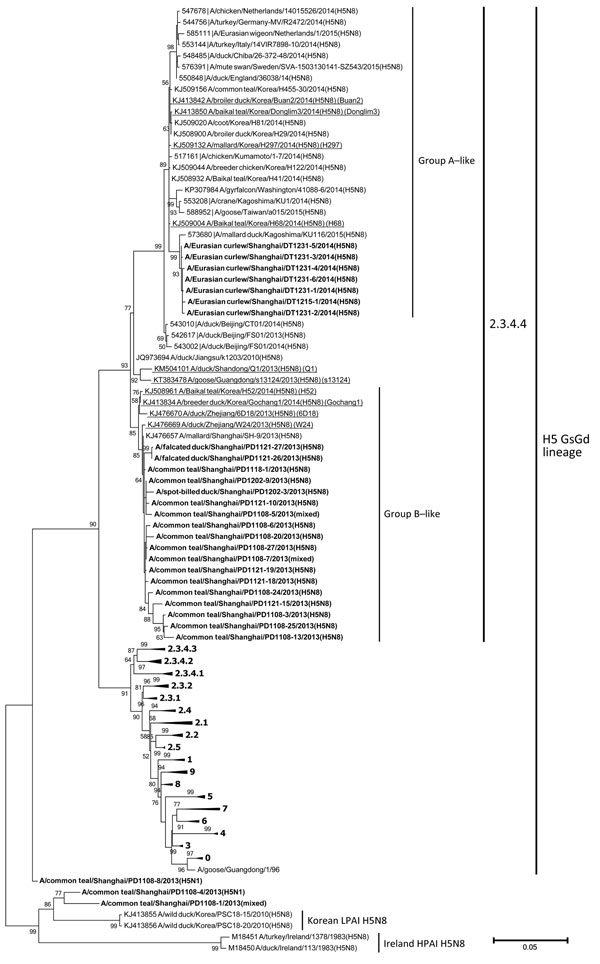
Figure. Phylogenetic tree of the hemagglutinin (HA) genes of influenza A subtype H5 viruses from wild birds of Shanghai, China, 2013–2014. Boldface indicates viruses from this study; representative isolates are underlined and referred to in abbreviated form in brackets. A total of 109 HA gene sequences (≥1,594 nt) were used for tree reconstruction. Representative strains and clades are recommended by WHO/OIE/FAO H5N1 Evolution Working Group and were retrieved from Influenza Virus Resource Database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/FLU/Database/select.cgi) and GISAID’s EpiFluTM Database (http://platform.gisaid.org/epi3/frontend). The phylogenetic tree was constructed by using the maximum likelihood method based on the general time reversible model with bootstrap analysis (100 replicates), by MEGA version 6 (http://www.megasoftware.net/). Bootstrap values ≥50% are shown. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. (See Technical Appendix.)
Main Article
Page created: May 17, 2016
Page updated: May 17, 2016
Page reviewed: May 17, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
