Volume 22, Number 8—August 2016
Dispatch
Lyssavirus in Indian Flying Foxes, Sri Lanka
Figure 2
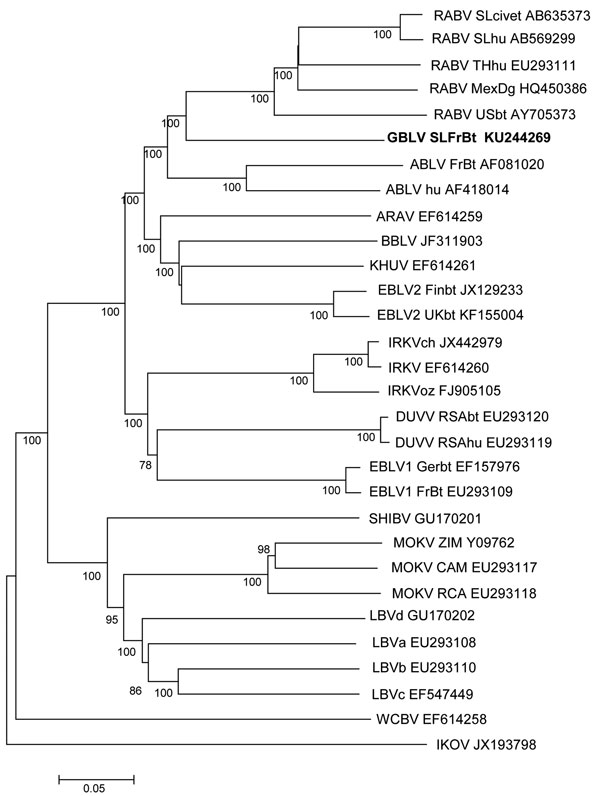
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships between representatives from all classified lyssaviruses and novel Gannoruwa bat lyssavirus (GBLV) on the basis of complete genome sequences. All 4 GBLV sequences form a monophyletic clade and are >99.9% identical across the genome; therefore, only 1 sequence (in bold) is shown. Relationships are shown as an unrooted phylogram, which was constructed by using the maximum-likelihood method and a general time reversible plus gamma distribution plus proportion of invariable sites model, and are identified by using the model test implemented in MEGA6 (http://www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap values ≥70 (1,000 replicates) are indicated next to branches; sequences are listed with GenBank accession numbers. RABV, rabies virus; ABLV, Australian bat lyssavirus; ARAV, Aravan virus; BBLV, Bokeloh bat lyssavirus; KHUV, Khujand virus; EBLV, European bat lyssavirus; IRKV, Irkut virus; DUVV, Duvenhage virus; SHIBV, Shimoni bat virus; MOKV, Mokola virus; LBV, Lagos bat virus; WCBV, West Caucasian bat virus; IKOV, Ikoma lyssavirus. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.