Volume 23, Number 3—March 2017
Research Letter
Fungal Contamination of Methylprednisolone Causing Recurrent Lumbosacral Intradural Abscess
Figure
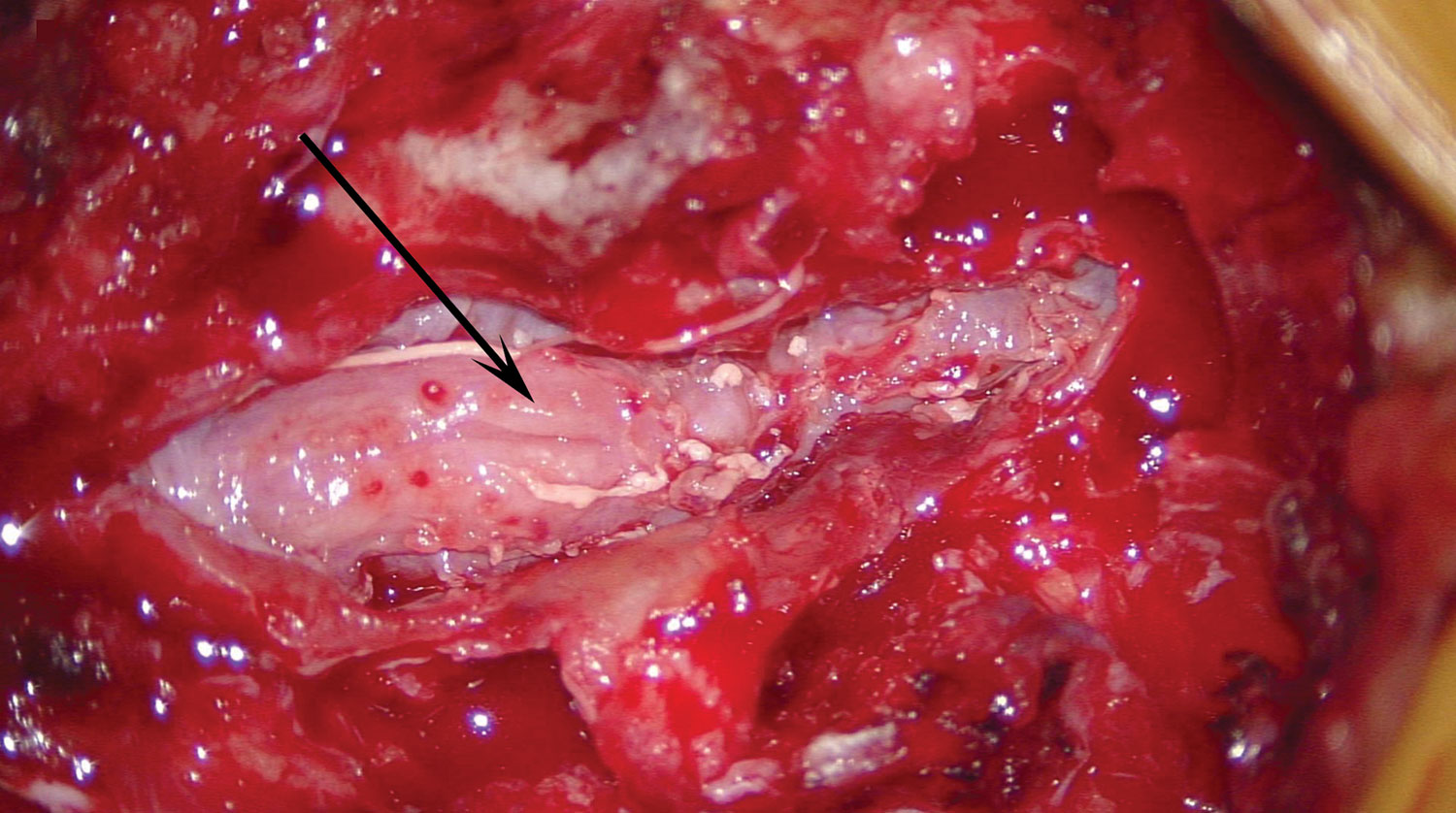
Figure. Intraoperative image demonstrating postevacuation cauda equina nerve roots that are grossly edematous and adherent (arrow), consistent with arachnoiditis, in a patient with recurrent infection from fungal-contaminated methylprednisolone, North Carolina, USA, 2015.
Page created: February 17, 2017
Page updated: February 17, 2017
Page reviewed: February 17, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.